Muscular System + Studies Flashcards
(17 cards)
different types of muscle
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal muscle
aka: striated and voluntary - attach to skeleton - striated b/c mm fibers striped - tires easily - contract w/ great force &rapidly

Anatomy of skeletal MM
*know this diagram*
actin + myosin = myofilament

endomysium
- btw muscle fibers
- encloses each mm fiber (wraps around each)
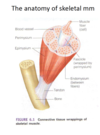
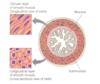
perimysium + fascicle
wraps, bundles and covers several sheated fibers together
- this forms the fascicle
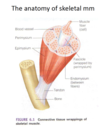
epimysium
a bunch of fascicles wrapped together
- this covers the entire length of the mm
- tapers into a tendon which attaches to bone

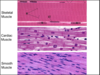
smooth mm
NO striations
Involuntary
Visceral
found in “hollow tubes” of visceral organs (stomach, bladder, respiratory passages)
Propels food and substances through

2 layers of smooth mm
circular layer
longitudinal layer
- allows mm to alternately contract and relax so they can move food through
cardiac mm
found only in heart
Striated
Involuntary
intercelated discs
mm contracts >> becomes smaller thus forcing blood into the arteries leaving the heart
Usually contracts @ steady rate
4 Skeletal MM functions
- Produce movement
- Maintains posture
- Stabilizes joints
- Generates heat (by product of ATP, 3/4 of energy escapes as hear)
- skeletal mm is 40% body’s mass
muscle for stabilization study
- muscle stabilization is key for spinal and joint health
- trunk mm imbalance and risk factor of low back pain
- low score had 340% increase risk for lower back pain
chronic low back pain
causes deficits in trunk mm strength
- normal extensor mm to flecor mm ratio is 1.2-1.5, but there is a deficit in lumbar extensors for clbp
- multifidi are used mostly hen the spine is extension
- fatty infiltration of lumbar extensors seen on MRI
- more severe BP - more atrophy and fat in mm
- adjustments and rehabilitation helps improvement
lumbar spine and sacrum study
intertrasversarri and interspinales mm act as large propreoception transducers (balance center)
- they send feeback to brain via mm spindles
- Failure to recruit these mm > LBP, weak mm, poor stabilizers, inadequate protection, microtrauma
if spine is moved out of place…
if spine goes out of place, nerve goes, and then muscle cant respond properly
lumbar dorsal ramus syndrome
when a nerve shuts down, muscle cant respond.
caused by subluxation (abnormal motion) and misalignment
use stregnth, neurological traning, adjustements to help, prevent, and manage
Myasthenia gravis
chronic autoimmune disorder - failure in transmission of nerve impulses to muscles - persistent muscular weakness and easily fatigued
parkinson’s disease
neurodegenerative disease
cell death in brain and presence of Lewy bodies in neurons
stiff and acing muscles bc they cant normal relax


