Musculoskeletal System Flashcards
(23 cards)
What are three types of bone disease
Congential
Acqiured
Inflammatory
Two congenital bone diseases include:
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteopetrosis
Two acquired bone diseases include:
Osteoporosis
Paget’s disease
(Osteitis deformans)
An example of an inflammatory bone disease is _____
Osteomyelitis
ID this bone disease

Osteogenesis Imperfecta
“Brittle Bone Disease”
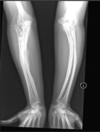
Describe OI
What is the pathogenesis of OI?

A group of hereditary conditions characterized by abnormal development of Type I collagen
Pathogenesis:
Gene mutations in the coding sequence of Type I collagen
Clinical issues and features of OI:
Bone fractures occur with minor trauma
Orally: “dentinogenesis imperfecta,” defective dentin
Hearing loss
Blue sclera - caused by decreased sclera collagen
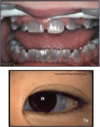
What is Osteopetrosis?

“Stonebone”
Reduced osteoclast-mediated bone resorption with defective bone remodeling
Bone is easily fractures like a piece of chalk
Marked increase bone density on radiographs
Clinical features of Osteopetrosis:

Fractures
Cranial nerve problems due to compression from surrounding bone
Obliteration of bone marrow

What can obliteration of bone marrow lead to in Osteopetrosis?
Reduced hematopoiesis
Recurrent infections
Normocytic anemia
What is Osteoporosis?
A disease characterized by increased porosity of the skeleton resulting from reduced bone mass

Characteristics of Osteoporosis
Spine and femoral neck are prone for fractures
Idiopathic or secondary to corticosteroids or multiple myeloma

Morphology of Osteoporosis
Bony trabeculae are thin and widely spaced leading to an increased susceptibility to fracture
Severe in vertebral bodies and femoral necks (weight- bearing bones)
Mineral content is normal

Clinical course and Treatment of Osteoporosis
Loss of height and kyphoscoliosis
Femoral neck fractures results in immobilization may lead to pulmonary embolism and pneumonia
Tx: Calcium and Vit D supplementation
Weight bearing exercise
Biphosphonates - decrease osteoclast-mediated bone resorption

Why should a dentist beware of bisphosphonates?
Inhibitors of osteoclastic activity and bone remodeling
Jawbone surgery should be approach with caution
Jawbone problems due to IV use principally
- Osteochemonecrosis

Paget’s Disease (Osteitis Deformans) is characterized by:
Frenzied osteoclastic activity followed by exuberant bone formation by osteoblastic activity
The excess bone is architecturally abnormal and unstable
Pathogenesis of Paget’s Disease (Osteitis Deformans):
Idiopathic
Possible paramyxovirus association
What are the three phases of development of Paget’s Disease?
Osteoclastic: Bone loss, Hypervascularity
Osteoclastic and Osteoblastic
Osteoblastic: Formation of dense, mineralized bone

Features of Paget’s Disease

Uncommon before 40
Male > Female
Bone lesions may be solitary (monostotic) or multifocal (polyostotic)
Most cases of Paget’s disease are ___ostotic
Polyostotic
Most common locations for Paget’s Disease
Spine
Skull
Pelvic bones
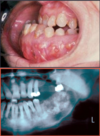
Major Clinical Features of Paget’s Disease
Bone pain = MOST COMMON
Secondary osteoarthritis
Bony deformity (bowing)
Excessive warmth (hypervascularity)
Neurologic complications (neural tissue compression)

Diagnosis of Paget’s Disease
Elevated serum alkaline phosphate (due to increased osteoblastic activity)
Serum calcium and phosphate = normal
1% develop an osteosarcoma (usually in pelvis; poor prognosis)


