Mycology Flashcards
(9 cards)
Difference between mould-like and yeast-like fungi?
Mould like have hyphae (mass of intertwined hyphae = mycelium) [septate or aseptate]
Yeast-like have round cells (replicate by fission or budding. (can involve pseudohyphae formation where budding cells don’t detach immediately)
What are asexual spores called? (special names?)
Conidia (held on conidiophores)
Sporangium is a sac full of spores. (held on sporangiphore)
Particular genera (like candida) have special names for their spores (chlamydospore, often multicellular)
What is SDA? (sabouraud’s dextrose agar)?
and what is use of LactoPhenol cotton blue preparation?
Fungal culture medium
Low pH, high glucose, peptones (aa polypeptide mixture)
LPCB preparation used to stain fungi, for identifying genera
Describe dermatophytes and their infections:
And diagnostic tools? treatment?
Dermatophytes cause Dermatophytosis/tinea/’ringworm’.
Infection of keratin rich areas: keratophilic/keratolytic
Skin, nails, hair
3 genera (Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporon)
Anthropophilic infections harder to treat than zoophilic or geophilic.
Diagnosed using SDA (sabouraud’s dextrose agar) culture, LPCB (lactophenol cotton blue stain), and KOH (potassium hydroxide preparation)
Treatment with topical or systemic antifungals (targeting ergosterol)
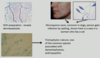
Antifungal mechanisms of action?
Targeting synthesis of fungal cell membrane component ‘ergosterol’
Lamisil contains: Terbinafine (prevents squalene to squalene epoxide)
Canesten contains an Azole (clotrimazole)
[Griseofulvin oral agent sometimes used, targets microtubule formation]
Candida and its infections:
3 Treatment types?
Candida albicans is dimorphic (mould or yeast forms)
Typical commensal on moist skin or mucous membranes.
Infections occur when immunocompromised in some way: diabetic/hospital urine infections, vaginal thrush, following Abx use (reduced competition), HIV [oral thrush, Esophageal candidiasis, candidaemia - 50% mortality!]
Treatment:
Polyenes (nystatin or AmphotericinB) bind to ergosterol in membrane, make it rigid –> makes pores, leaks K+
Azole: Fluconazole.
New antifungal! Echinocandins: Caspofungin (inhibits Beta-glucan synthase, a fungal specific cell wall component)

Describe 3 other opportunistic fungal pathogens other than Candida:
How are they treated?
Cryptococcus: yeast form fungus causes cryptococcosis. Found in bird droppings (spores can be inhaled) migrates to CNS can lead to meningitis in severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. AIDS)
- *Aspergillus**: mould form fungus, inhaled as spores into lungs. Leads to 1) Hypersensitivity aspergillosis (asthma-like)
2) Non-invasive aspergilloma [in cavity left by TB!]
3) Acute Invasive aspergillomas: pneumonia, common in immunosuppressed patients
Pneumocystis jirovecii: yeast-form (previously considered a protozoan and it is sensitive to antibiotic Cotrimoxazole) –> pneumocystis pneumonia PCP.(immunosuppression and also COPD risk factors)

Main trigger to change between fungal forms (mould and yeast) in dimorphic fungi? and examples of dimorphic fungi?
Temperature (37deg tissue temperature –> yeast form)
25deg environmental temperature mould/mycelial form
Dimorphic fungi: Candida albicans and Histoplasma capsulatum (USA var capsulatum [pulmonary/disseminated infections], africa var duboisii [bone and skin infections])

Histoplasma capsulatum infection pathogenesis?
Dimorphic fungus: common in USA, spread by bird or bat droppings (aerosolised microconidia of mycelial/mould form)
Microconidia phagocytosed by macrophages in lung.
Within macrophages conidia transform into yeast phase of life cycle. (decrease dectin-1 recognisable B-glucan, replaced by alpha-glucan synthase; calcium-binding protein-1 helps survival in macrophages, modulating lysosomal pH)
Multiply in macrophages and disseminate throughout body. Normally cell-mediated immunity eradicates after possible flu-like illness (with large infectious dose, many/50-80% people in USA exposed at low dose –> asymp).
var capsulatum in america –> pulmonary (rarely fibrosis) (disseminated in HIV/immunocomp patients = fever fatigue, hepatosplenomegaly, weight loss) (diagnosed from sputum sample, 2 cultures at 37 and 25deg)
var duboisii in africa (skin and bone lesions, treat with itraconazole) (diagnosed by bone marrow aspirate)