Mycology Flashcards
(50 cards)
fungi, generally
eumycota
process of gaining nutrition through absoption rather than ingestion
absorptive nutrition
the process of fungal gorwth by formation of hyphae
hyphal growth
long branching stucture made up of hyphae
mycelium (pl.mycelia)
a reproductive unit of some fungi
conidia
multinucleated cell where the nuclei came from genetically distint individuals
heterokaryon
infection caused by the fungi
-iasis
disease caused by the fungi
-mycosis
what arethe two forms of fungus?
- filamentous molds
- unicellular yeast
A drug was made to target chitin, glucan and mannan. What is this drug targeting?
cell wall of fungus
a drug was designed to target ergosterol, what is this structure?
Plasma membrane of fungus
how do fungus eat?
absorptive nutrition- fungis cell walls cannot break apart, so they send out digestive enzymes and absorb the broken down products.
what are the two phases for fungus?
vegitative-reproductive
absorbing-spreading
a drug destroys the calcium gradient and k+ uptake proteins in a fungus What is affected?
Hyphal gorwth(hyphal extension)- vesicles from the golgi fuse to the cell membrane to allow expansion. The turgor pressure allows the fungus to penetrate tough material such as wood.
Turgor pressure is regulated by H+ export and K+ uptake. Ca 2+ released by the ER and mitochondria induces vesicles to fuse and to expand the plasma membrane at the growing tip.

correlate hyphal growth and nutrient uptake
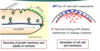
a drug targets the destruction of hyphal tips, what is affected?
the hyphal growth uses the tips to elongate. The absroptive zone is nearest to the hyphal tip.
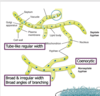
the molds can have hypha that are septate(shown in photo) or nonsepate
- the septa forms to partially compartmentalize the cytoplasm

aspergillus and penicillin aka
fillamentous fungi called molds
What is a coenocytic species?
multinucleate species that can grow with out undergoing cytokinesis.
these lack septa. compared to the septate hyphae in the photo
single extension on the fungus, location os growth vs characteristic, round fuzzy colony
hypha
mycelium-form the characteristic round, fuzzy colony of fungus

describe the reproduction cycle of aspergillis

A drug targets the CAT of spore/conidia germination. Explain
Conidial anastomosis tubes- fusion between conidia and conidial germlings .
wider the germlings are growing away from eachother. Most CATs are formed directly fron conidia but some also form germ tubes.

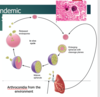
after observing arthrospores under the microscope sample, the doctor determined that it was a ___
fungus,
athrospores -section of hyphae break off at septa.
Coccoidioides replicates in this manner
a dermatophyte that lives on the skin
tinea pedis(athletes foot), Trichophyton rubruum( ringworm- live on cats ),
a sample shows a sprangia, what could it be from if it was growing on bread?
Sporangia- (spherules and endorspores) -asexual spore structures from rhizopus (bread mold) or from zygomycetes