Virology Flashcards
(35 cards)
define and explain the following terms
- virus
- viroids
- virusoids
- prions
- virus
- ribosomal parasite
- viroids
- naked RNA that infect plants
- virusoids
- RNA, coated with protein, from a neighboring plant
- the RNA does not encode for any protein
- RNA, coated with protein, from a neighboring plant
- prions
- infectious proteins
- misfolded, very protease resistant proteins
- mediate the misfolding of other host proteins
what are the types of interferon? 1, 2,3
purpose?
- IFN
- alpha-all cells, triggered by dsRNA
- beta-all cells, triggered by dsRNA
- IFN gamma
- Tcells, NK cells-triggered by antigen, mitogen, IL-2,12
- IFN lambda
- 1,2,3 = IL-29/28a/28b
- coexpressed with type 1 IFN, sounds like these are required
- signal independent of Type1-a/b
IFN are not expressed regularly, they are usually repressed via repressor
- purpose
- a/b- go to neighboring cells and tell them to prepare for viral invasion
*
- a/b- go to neighboring cells and tell them to prepare for viral invasion
what is the reason that 70% of viral infections are subclinical?
Type 1 (A/B) IFN
-go to neighboring cells and allow themto prepare defenses
what is the goal of IFN expression?
what targets dsRNA
shut down the cell translation machinery- no virus replication
dsRNA is targeted by PKR, which increases in expression
what is the function of PKR
PKR monomers bind to dsRNA.
when bound, the domains of PKR conform and the catlytic domains can be phosphorylated.
cross phosporylation leads to the ability to phosphorylate and shut down other substrates:elongation factor 2 (eLF2)

WHICH interfeon stimulates the adaptive immune system?
Type 1 IFN stimulates the adaptive immune system
Type2 is the most important in stimulating the lymphocytes.
what are common side effects of interferon?
fever, malaise, fatigue, muscle pains,
toxicity to: kidney, liver, bone marrow, heart
describe the pathway for interferon activation
Type 1 and 3 interferons initiate the same intracellular response through two different receptors:
Type1: a/b,
Type3:lambda

what are the cytopathic effect that are associated with different virus infections
cell death: apoptosis, pyroptosis, necrosis, syntia formatiton, inclusiong bodies
syncytia- multinucleated cells. formed when cells fuse together
explain when can Cytopathic effects be seen in a culture
cpe in cultured cells between 5-15 days
what are direct test(6)? Indirect tests(4)?
- direct-presence of virions, virus proteins or virus genomes
- CPE
- PCR
- RT-PCR
- Fluorescence assay- detects the virus in infected cells
- snadwich ELISA
- Hemagglutination assay
- indirect- presence of Ab
- Western blot (HIV)
- indirect ELISA
- Heamagglutination inhibition assa
- virus neutralization assy
explain how to read and inerpret the hemagglutination assay and hemagglutination inhibition assay

the top is hemagglutination assay, bottom is hemagglutination inhibition assay
- reading
- HA- virus of various dilutions are mixed with consistent sample sizes of chicken blood.
- sample A causes hemagglutination up to a dilution of 1:256 dilution;HA titer causes hemagglutination up to a certain dilution and the last reading = the virus stock
- sample A
- dilution up to 1:256= titer of this virus stock = 256
- sample b and c
- dilution up to 1:128= titer of the virus stock = 128
- sample A
- sample A causes hemagglutination up to a dilution of 1:256 dilution;HA titer causes hemagglutination up to a certain dilution and the last reading = the virus stock
- HI- dilutions of patients serum are performed and added to consistent samples of virus in blood.
- there is enough Ab in the patients serum to keep the virus from causing hemagglutination.
- sample shows a dilution of 1:160 allows for viral hemagglutination.
- dilution up to 1:80=titer of Ab is 80
- sample shows a dilution of 1:160 allows for viral hemagglutination.
- there is enough Ab in the patients serum to keep the virus from causing hemagglutination.
- HA- virus of various dilutions are mixed with consistent sample sizes of chicken blood.

The hemagglutination inhibition assay was performed on serum sample. what are the patients titers the first and second time.
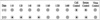
<10 on 1/12; 80 on 2/15
list the DNA viruses and their disesaes
- PPPAHHP
- Parvo-ss(+/-)
- linear
- disease
- parvo
- erychrovirus
- polyma -DS
- cicular
- disease
- BK virus-kidney disease
- JC virus-progressive brain disorder
- Papilla-DS
- circular
- disease
- HPV
- warts
- cancer
- HPV
- adeno-DS
- linear
- disease
- serotype- dependent (GI, respiritory, conjuctiva)
- Hepadna-DS
- circular-gapped
- disease
- Hepatitis B
- herpes-DS
- linear
- disease
- alpha
- HSV1-cold sores
- HSV2-genittal herpes
- VZV-chicken pox
- beta
- HCMV/HHV6/HHV7
- gamma
- EBV
- HHV8/KSHV
- alpha
- pox-DS
- covanalent
- disease
- small pox
- money pox
- molluskum contagiosum
- Parvo-ss(+/-)
what type of viruses have a necleocapsid?
all helical viruses
RNA only
- Corona, Filo, Rhabdo, Arena, Bunya, Peramyxo, Orthomyxo
Diagram the replication cycle of the adenovirus

A patient was exposed to the chicken pox and never experienced and episode. Diagram the two cycles and explain this patients current state.
VZV is part of the herpes family wich is known for lysogenic and lytic cycles.
lysogenic (left) The Latency Associate Transcript is transcribed and forms a lariat, stopping the continuation of immediate early and early transcription.
Lytic (Right) similar to the adeno virus, only the last step would be for several cycles of golgi/ER to collect all the necessary proteins in the tegument.

list the RNA viruses, and relevant information
RNA
- Rheo
- DS-
- disease
- Rotavirus
- gastroenteritis
- Rotavirus
- hepe/cilici
- SS
- disease
- hepetitis E
- noro virus-gastroenteritis
- Pico
- SS
- disease
- hepatits A
- Entero virus
- polio
- echovirus
- coxsackivirus- hand/foot virus
- Flavi
- SS
- disease
- Hep C
- yellowfever
- dengue virus
- west nile
- Zika
- Toga
- SS
- disease
- rubella
- alpha virus-mosquito
- chikungunya
- very old and young
- Retro
- SS-2 copies
- disease
- HIV
- corona
- SS
- disease
- corona- cold, SARS, MERS
- filo
- SS
disease- ebola
- SS
- Rhabdo
- ss
- disease
- rabies
- arena
- ss-2seg
- disease
- alot
- Bunya
- ss-3 seg
- disease
- hanta
- paramyxo
- ss
- disease
- measles
- mumps
- paramyxo
- RSV
- orthormyxo
- ss-8seg
- disease
- influenza
what the the following receptor correspond with?
- CAR
- HVR
- CD4/CCR5/CXCR4
4.
- adenovirus-
- Heparin-sulfate, herpes virus receptor- herpes
3.
describd the cycle of polio
- attachment/entry
- uncoating
- translation of mRNA to poly protein
- polyprotein cleavage
- RNA amplification
- virus assembly and release

of the following which can use host cell machinary and which need to generate their own polymerases? explain
- adenovirus
- Herpes simplex virus
- Polio
- Rabies
- HIV
- adenovirus
- go into the nucleaus and use host cell machinary for transcription and translation
- herpes simplex virus
- go into the nucleus and use host cell machinery for transcription and translation- lytic
- lysogenic, LAT-lariat is formed and DNA circularizes, suppressing transcription
- polio
- +SS, can use host cell machinary upon entry in to host cell
- rabies
- -SS, but is introduced with viron polymerases assembeled.
- once the +mRNA is transcribed, by the viron polymerase, then host cell machinary translates the +mRNA
- HIV
- the virus has in intorduced to the cell with reverse transcriptase in tacked.
2.
- the virus has in intorduced to the cell with reverse transcriptase in tacked.
describe the HIV infection cycle
- atttachment to cells andbinding to receptors:
- CD4
- CXCR4
- CCR5
- MEMBRANE fusion and capsid and nucleocapsid release
- reverse transcription, nuclear import and proviral DNA integration
- Transcription and translation of viral genes and replication of the genome
- assembly of progeny virions
- budding of progeny virions
Describe the rhabdovirus replication cycle
- attachment/entry
- uncoating
- transcription
- translation
- tranlsation of viral envelope glycoprotein
- genome amplification
- envelope glycoprotein glycosylation, maturation
- envelop glycoprotein trafficking to cell membrane
- virus assembly and release
an increase in temperature of the host, is to combat what viral replication cycle? explain
Viral assembly will be affected, as the heat makes the stochastic assembly of the structures more difficult.
The capsid will undergo regular generation at optimal temperatures.