Myeloid Neoplasms Flashcards
(43 cards)
Characterization of acute myelogenous (myeloid) leukemia? (AML)
Accumulation of immature myeloid precursors in the BM and suppression of normal hematapoiesis
Characteristics of Myelodysplastic syndromes?
Ineffective hematopoiesis with cytopenias
Characterization of chronic myeloproliferative disorders (CML)?
Increased production of terminally differentiated myeloid cells
What is found in the BM in AML?
Undifferentiated blasts
(results in anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia)
Diagnosis of AML?
Myeloid blasts >20% of marrow cells
M1 myeloblast characteristics in AML?
- Delicate chromatin
- 2-4 faint nucleoli
- Cytoplasm with azurophilic peroxidase positive granules
M3 acute promyelocytic leukemia cell characteristics?
- Auer rods (definitive evidence)
- Peroxidase positive
M5 monoblast cell characteristics in AML?
- Folded/lobulated nuclei
- Esterase positive
- NO auer rods or peroxidase
AML cell markers?
- +CD34 (multipotent stem cell marker)
- +CD33 (immature myeloid marker)
- -CD64 (mature myeloid)
What is this? What can you distinctively see that indicates that?

Acute promyelocytic leukemia, M3
Can clearly see the Auer Rods
What is this?

AML, M1
Can see the faint nucleoli
Dispersed chromatin
What is this?
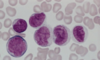
AML M5
The nuclei are lobulated/folded.
AML signs and symptoms?
- Pancytopenia
- Weakness, fatigue, infections, and bleeding
- Less extramedullary tissue infiltration in comparison to ALL
- M4/M5 differentiation:
- Infiltration of the skin and gingiva may occur
(60% remission with therapy; only 15-30% disease free after a year)
Bone marrow in Myelodysplastic Syndromes? (MDS)
What are the two forms?
Marrow is partly or completely replaced by the clonal progeny of a defective stem cell
- 2 forms
- Idiopathic
- Therapy related (2-8 yrs after cancer therapy)
- More rapid transformation to AML
MDS clinical presentation? Survival?
- Weakness
- Infections
- Hemorrhages
- Survival = 1-2 years
MDS:
Describe A?
B?
C?
D?

- A
- nucleated RBC progenitors
- B
- Ringed sideroblasts
- Iron in mitochondria (stains blue)
- C
- Neutrophils with only 2 nuclear lobes
- D
- Megakaryocytes with multiple nuclei
4 most common syndromes of chronic myeloproliferative disorders?
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Polycythemia vera
- Essential thrombocytosis
- Primary myelofibrosis
Simmilar characteristics in the chronic myeloproliferative disorders?
- Stem cells circulate and initiate extramedullar hematopoiesis
- Organomegaly
- All can progress to acute leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML):
Cause?
- Philadelphia chromosome 9:22 translocation
- c-abl proto-oncogene (9)
- bcr 22
- transposition yields tyrosine kinase activity
CML leukocytosis cells?
Neutrophils
Metamyelocytes
Myelocytes

CML presentation?
Treatment?
- Presentation
- anemia, fatigue, weight loss, anorexia
- splenomegaly
- Treat
- imatinib
CML types of blast crises?
- 70% myeloblast
- AML-like
- ALL-like
- Tdt
- CD10
- CD19
Polycythemia vera:
Cells produced?
Increased production of erythroid granulocytic, and megakaryocytic progenitors.
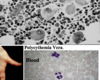
Presentation of polycythemia vera?
- Erythrocytosis, granulocytosis, and thrombocytosis in peripheral blood
- Erythromelalgia
- burning pain in feet/hands with erythema, pallor, or cyanosis
- Abnormal blood flow: bleeding and thrombosis
- Marrow fibrosis
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis –> hepatosplenomegaly





