Neuroanatomy Class Exam 1 Flashcards
(180 cards)
Where does the CNS bend occur?
At the cephalic flexure
Where is the Cephalic Flexure Visible?
It is visible at the junction between the brainstem and the diencephalon
What are the divisions of the brainstem?
Midbrain, Medulla, and Pons
What joins the two cerebral hemispheres?
The Corpus Callosum; this is a huge fiber bundle
What develops into the ventricular system?
The cavity of the neural tube
How does the system of ventricles connect?
The third ventricle opens into the lateral ventricle (of each hemisphere) through the inerventricular foramen. Posteriorly, the third ventricle is continuous with a narrow channel through the midbrain known as the cerebral aqueduct. This aqueduct connects with the fourth ventricle of the pons and medulla. The fourth ventricle is continuous with the central canal of the caudal medulla and the spinal cord.
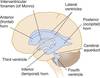
What is burried deep within the lateral sulcus?
The insula is hidden within this sulcus. It overlies the site where the telencephalon and the diencephalon fuse during embryological development.
What is the circular sulcus?
The circular sulcus outlines the insula and marks its borders withe opercular areas of the cortex.

What are the four divisions of the frontal lobe?
The Superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri. The fourth major division is the

What does the frontal lobe contain?
The frontal lobe mainly contains the motor areas.
What are the subdivions of the parietal lobe?
1) Postcentral sulcus and gyrus
2) Superior Parietal Lobule
3) Supramarginal Gyrus
4) The Angular Gyrus
5) The Precuneus (only visible on the medial surface of a sagittal cut)

What is the parital lobe mainly responsible for?
Integrates sensory information
What are the subdivisions of the Temporal Lobe?
These include the superior, middle, and inferior temporal gyri as well as the occipitotemporal gyrus and the inferior temporal gyrus. The last two are only visible medially with a sagittal cut and viewed from slightly below the brain.

What is the temporal lobe primarily responsible for?
It contains the auditory areas.
What are the subdivisions of the Occipital Lobe?
These include the lateral occipital gyri, lingual gyrus, and the Cuneus.

What is the occipital lobe mainly responsible for?
Primary responsiblity is vision
What are the subdivisions of the Limbic Lobe?
These include the Cingulate sulcus and gyrus, the Uncus, and the Parahippocampal Gyrus.

What is the Limbic Lobe primairly responsible for?
Primary responsiblity is emotion and memory processing.
What does the Diendephalon include?
The thalamus and hypothalamus.
What is the function of the thalamus and the hypothalamus?
The thalamus serves as a relay center for sensory information to the cortex. All sensory info goes through the thalamus except taste and smell. It also regulates consciousness and alertness.
The hypothalamus is responsible for autonomic actions, such as controlling body temperature, heart rate, and hunger.
Where are most cranial nerves located?
Most cranial nerves are located in the brainstem
What are the three functions of the parietal lobe?
1) Primary Somatosensory Cortex
2) Langauge Comprehension (inferior parietal lobule of one hemisphere paired with portiosns of the temporal lobe)
3) Spatial Orientation adn direction of attention
What is the interthalamic adhesion?
The point of fusion for the two thalami
What is one exception to sensory information that does not go through the thalamus?
Olfactory Information; all other information goes through the thalamus












































