Neuroanatomy Exam 2 Flashcards
(176 cards)
Why are arteries black on a T2 weighted MRI?
Fluids are usually white on a T2 MRI. However, the blood within arteries is moving relatively quickly, which makes it appear darker on the image.
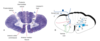
What regions of the brain (think vesicles) do the internal charotid arteries supply?
Most of the telencephhalon and diencephalon
What does the vertebral system supply?
Brainstem, cerebellum and parts of the diencephalon, spinal cord, and occipital and temporal lobes
Desrcibe the path the internal chharotid artery takes to reach the brain.
Ascends through each side of the neck, traverses the petrous temporal lobe, passes through the cavernous sinus, and finally reaches the subarachnoid space at the base of the brain
What is the ophthalamic artery?
Off shute of the internal charotid artery as it leaves the cavernous sinus. This artery travels along the optic nerve to th orbit to supply the eye and other orbital structures.
What happens after the internal charotid artery passes the optic chiasm?
Bifurcates into the middle and anterior cerebral arteries
Which artery is often involved in cerebrovascular accidents?
The anterior choroidal artery
What artery supplies the amygdala and portions of the internal capsule?
Anterior Choroidal Artery
What artery supplies the optic tract?
Anterior Choroidal Artery
What artery supplies the choroid plaxus of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle?
Anterior Choroidal Artery
Describe the general travel of the posterior communicating artery.
Passes posteriorly, inferiorily to the optic tract and toward the cerebral peduncle. Joins the posterior cerebral artery

What connects the two anterior cerebral arteries?
Anterior Communicating Artery

What structure does somatosensory information have to pass through going from the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex?
The internal capsule
What are lenticulostriate arteries?
Branches of the middle cerebral artery that penetrate the brain near their origin and supply deep brain structure of the telencephalon and diencephalon

Where doo the two vertebral arteries fuse to give rise to the basilar artery?
At the junction of the pons and medulla
What branches does the vertebral artery give rise to?
Posterior Spinal Artery
Anterior Spinal Artery
Posteriior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
(Each one gives rise to these 3)
What does the posterior spinal artery supply?
The posterior third of the spinal cord
What does the anterior spinal artery supply?
Anterior two thirds of the spinal cord
What does the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) supply?
Much of the interior surface of the cerebellar hemispheres

What artery supplies the more anterior portions of the inferior surface of the cerebellum (like the Flocculus) and parts of the caudal pons?
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA)

What does the superior cerebelar artery supply?
the superior surface of the cerebellum and much of the caudal midbrain and rostral pons
What artery supplies the inner ear?
Internal auditory/labyrinthine artery; occlusion can lead to vertigo and ipsilateral deafness
Which artery sends branches to the thalamus and the splenium?
Posterior Cerebral Artery
What do the posterior choroidal arteries supply?
Choroid plexus of the third ventricle and body of the lateral ventricle