Neurology Flashcards
(109 cards)
ANATOMY & BLOOD SUPPLY
•Blood Supplies to the brain
–Frontal – Anterior Cerebral Artery
–Parietal – Anterior & Middle Cerebral Artery
–Temporal – Middle Cerebral Artery
–Occipital – Posterior Cerebral Artery

Lobes of the brain
•Lobes of the the brain
–Frontal
–Parietal
–Temporal
–Occipital
FRONTAL LOBE FUNCTION
Dr. Brain - higher level thinking
•Frontal Lobe
–Personality
–Reasoning
–Motor planning
–Judgment
–Emotional regulation
TEMPORAL LOBE FUNCTION
MEMORY - VISUAL - UNDERSTANDING AND COMPREHENSION
–Hearing
–Comprehension
–Visuospatial Orientation
–Conceptual Understanding
–Visual Memories/Visual Processing
PARIETAL & OCCIPITAL LOBE FUNCTION
•Parietal Lobe
–Pain
–Touch (all types)
–Temperature
–Pressure
•Occipital Lobe
–Sight
RIGHT BRAIN FUNCTION
RIGHT = PERCEPTION
•Right side
–Non-verbal and artistic abilities.
- Visuo-perceptual function (hand-eye coordination)
- Spatial relationships
- Perception of one’s position in space
- Nonverbal communication (facial gestures)
- Judgment
- Self perception
LEFT BRAIN FUNCTION
2 Types of strokes
Ischemic stroke – Blockage
Hemorrhagic – Burst
Middle Cerebral Artery = 90% of cases
Aneurysm is BURSTING of the blood vessel
A patient is evaluated and is found to have drooping of the mouth on the right side but no significant drooping of the eyes are noted. The patient also has an incoherent speech but with a normal speed. Which of the following is the MOST likely present?
A) Right anterior cerebral artery stroke
B) Right Bell’s Palsy
C) Left middle cerebral artery stroke
D) Left Lateral medullary stroke
A: Causes stroke on the contralateral side.
B: Eyes are not drooped, Bells Palsy is eyes and face
C: CORRECT
D: Also know as a PICA stroke or Wallenburg stroke – causes facial dropping on the same side
MCA STROKE supplies what?
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) supplies the Temporal, parietal and parts of the frontal lobes
MCA supplies superior-lateral aspects of the parietal lobe
Therefore suplies teh UE and Face
“My Crappy Arm”
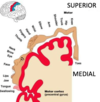
MCA Stroke Signs and Symptoms
Top 3 Signs and Symptoms
•Affects contralateral upper extremity more
•Affects contralateral lower face
•Affects right or left hemisphere causing variable symptoms
____
–Upper part of the face is NOT IMPAIRED
–Affects right or left hemisphere causing variable symptoms
- Broca’s / Wernicke’s Aphasia (Left side)
- Perceptual deficits (unilateral neglect) (Right side)
- Sensory Ataxia (left or right)
- Apraxia (left or right)
ACA STROKE supplies what?
- Anterior Cerebral Artery supplies the Frontal & Parietal Lobes
- ACA also supplies superior and medial aspects of the parietal lobe
–
So more LE is affected
“A Crappy Ass”
Motor or Somatosensory?
Precentral Gyrus
Post Central Gyrus
Precentral Gyrus – Motor
Post Central Gyrus - Somatosensory
ACA Stroke S+S
•Signs and Symptoms
–Affects contralateral lower extremity more
–Urinary incontinence
–Affects right or left hemisphere causing variable symptoms
- Ideomotor Apraxia
- Problems with imitation
- Akinetic Mutism
–
A patient presents with a left ACA stroke and is asked to utilize a comb to groom his hair. Despite demonstration and verbal cueing, the patient is unable to understand how the comb is used. Which of the following impairments is the patient MOST likely displaying?
A) Agnosia
B) Anosognosia
C) Ideomotor apraxia
D) Ideational apraxia
A: Inability to perceive objects or people
B: When pt can’t perceive that they have a illness (right sided perceptual problem)
C: Apraxia is inability to initiate the task (on demand) but if they have a specific que, they can.
D: Pt cannot perceptualize it at all.
A patient presents to the outpatient clinic six weeks post CVA displaying a primary LE flexor synergy pattern with some hip extension and knee extension movements. Which of the following Brunnstrom stages would you characterize this patient?
A) Stage 1
B) Stage 3
C) Stage 6
D) Stage 4
BRUNNSTROM STAGES
1.Flaccidity
2.Onset of primitive reflexes
3.Max spasticity
- Spasticity declines and some movements are performed out of synergy
- Selective control of movement
6.Near normal with coordinated motions out of synergy
7.Normal
–

SYNERGY
Group of muscles that work together as a unit to assist with some daily function (feeding, ambulation)
–

LOWER EXTREMITY SYNERGY - Flexion
Dog peeing on a fire hydrant
•FLEXOR
–Hip Flexion*
–Hip Abduction
–Knee Flexion
–Ankle Dorsiflexion
–Ankle Inversion
–Toe Extension
–

LOWER EXTREMITY SYNERGY - Extension
Michael Jackson
•EXTENSOR
–Hip Extension
–Hip adduction*
–Hip Internal Rotation
–Knee Extension *
–Ankle Plantarflexion *
–Ankle Inversion
–Toe Flexion
–

LOWER EXTREMITY DOMINANT
DOMINANT PATTERN
–Hip Flexion
–Knee Extension
–Ankle Plantarflexion
UPPER EXTREMITY SYNERGY - Flexion
•FLEXOR
–Scapular Retraction & Elevation
–Shoulder Abduction
–Shoulder External Rotation
–Elbow Flexion*
–Forearm Supination
–Wrist and Finger Flexion
–

UPPER EXTREMITY SYNERGY - Extensor
•EXTENSOR
–Scapular Protraction
–Shoulder adduction*
–Shoulder Internal Rotation
–Elbow Extension
–Forearm Pronation*
–Wrist and Finger Flexion
UPPER EXTREMITY DOMINANT
DOMINANT PATTERN
–Shoulder adduction
–Elbow Flexion
–Forearm Pronation
One particular PNF pattern that really does the trick.
D2 flexion








