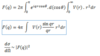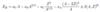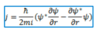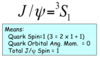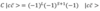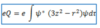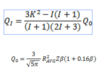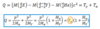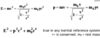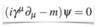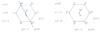Nuclear & Particle Physics Flashcards
How are orders determined in Feynman diagrams?
What are the quark compositions of the lightest known mesons, the pions (0, +, -)?

What are the quark compositions of the lightest strange mesons, the kaons (+, 0)?
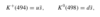
What are the rules of Feynman diagrams?
What is the overall effective coupling?
Why does the charged pion have longer lifetime than a meson in an excited state?
Why are some decays observed but not others?
What changes do you make to work in natural units?
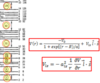
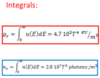
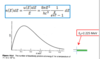
What is the scattering amplitude for the Yukawa potential?
What is the Yukawa potential?
How do you calculate the radius of scission?
- r = R0 A1/3
What is the centrifugal potential? When is it included?
How does the Q value change if centrifugal was accounted for in the potential?
What are the conservation laws involved in nuclear reactions?
*
What is the total energy of a particle?
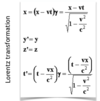
What is the Lorentz factor? How would distance change in relativistic kinematics compared to non-relativistic kinematics?
What makes something a strong interaction?
What are the conservation laws for weak interactions?
What is the liquid drop model for atomic nuclei?
What are the ordinary particles?
- electrons (electricity and chemical reactions)
- electron neutrino (billions pass through body all the time)
- up quark (+2/3 e)
- down quark (-1/3 e)
What are force particles? And what are they? Which kind of particles experience them?
- transmit 4 fundamental forces of nature
- gluons; strong => quarks
- explosive release of nuclear E
- photons; EM => quarks & charged leptons
- electricity, magnetism & chemistry
- (intermediate vector) bosons; weak => quarks & leptons
- W- W+ Z0
- some forms of radioactivity
- gravitons; gravity => all particles with mass
- all weight experienced is due to gravitational force
- gluons; strong => quarks
What is elastic scattering?
- only change in direction of momentum (not magnitude)
- i.e. magnitude of momentum before and that of after are the same
What is alpha particle scattering?
- size of nucleus
What is electron scattering?
- charge distribution (protons) inside nuclei