Ophthal Flashcards
(76 cards)
What screening should take place for patients with a family history of glaucoma?
Annual screening from the age of 40
What are the risk factors for POAG?
Genetics A-C Myopia HTN DM Steroids
What are the features of POAG?
Peripheral visual loss Reduced acuity Disc cupping +-pallor
How would you investigate for POAG?
Automated perimetry Slit lamp with dilatation Tonometry Central corneal thickness measurement Gonioscopy (measures peripheral anterior chamber configuration and depth)
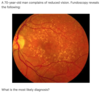
What are the fundoscopic features of ARMD?
Drusen - yellow areas of pigment deposition in and around the macula In wet ARMD, well demarcated red patches may be seen representing haemorrhages
What is the typical presentation of ARMD?
Subacute vision loss with: Reduced acuity Difficulties in dark adaptation Fluctuations day to day Photopsia
What are the key risk factors for ARMD?
Age>75 Smoking FHx HTN DM
What is the first and second line management of allergic conjunctivitis?
1st - topical or systemic antihistamines 2nd - topical mast cell stabilisers e.g. sodium cromoglicate
What is the management of ARMD?
Vit ACE for dry reduce progression VEGF useful in wet Laser photogoaculation is beneficial but risks acute visual loss
Whatis the goal of treatment in pOAG and what drugs are used?
To reduce IOP Beta blockers e.g. timolol PG analogues e.g. latanoprost Sympathomimetics e.g. brimonidine Carb anhydrase inhibitors - Dorzolamide Miotics e.g. pilocarpine
What are the different grades of hypertensive retinopathy, and name the grading system used?
Keith-Wagener classification 1 - Tortous vessels with silver wiring 2 - 1+ AV nipping 3 - 2+ Cotton wool exudates and flame/blot haemorrhages 4- 3+ papilloedema
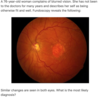
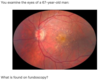
What is seen on fundoscopy of papilloedema?
Venous engorgement Loss of venous pulsation Blurring of optic disc margin Elevation of optic disc
What are the causes of papilloedema?
SOL Malignant HTN IIH Hydrocephalus Hypercapnia
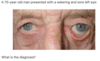
What are the features of an Argyll Robertson pupil?
Small irregular pupils which accomodate but do not respond to light
What is a Hutchinson’s pupil?
Unilaterally dilated pupil which is unresponsive to light. A result of compression of the occulomotor nerve of the same side, by an intracranial mass (e.g. tumour, haematoma)
What are the commonest causes of sudden painless vision loss?
Ischaemic/vascular (amaurosis fugax) Vitreous haemorrhage Retinal detachment Retinal migraine
What are the causes of vitreous haemorrhage?
DM bleeding diatheses Anticoagulation
What might patients with retinal detachment describe?
Dense shadowing that starts peripherally and progresses towards the centre Like a veil or curtein over the field of vision Straight lines may appear curved
What is the management of herpes zoster ophthalmicus?
Oral aciclovir
What are the two aims of treatment of acute glaucoma and how is this achieved?
Reduce aqueous secretion - acetazolomide Induce papillary constriction - topical pilocarpine
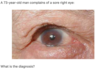
What are the features of acute closed angle glaucoma?
Severe pain Reduced acuity symptoms worse with mydriasis Hard red eye Haloing Non-reactive pupil Corneal oedema N/V +- abdo pain
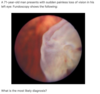
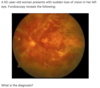
What is seen on fundoscopy of central retinal artery occlusion?
Cherry red macula on a pale retina
What ist he management of a stye?
Analgesia and hot compress
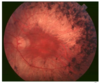
What distinguishes between non-proliferative and proliferative DMR?
Non-proliferative DMR shows microaneurysms, blot haemorrhages, hard exudates, cotton wool spots, venous bleeding et/ Proliferative DMR also shows neovascularisation +-viteous haemorrhage