Ophthalmology Flashcards
(63 cards)
Disadvantage if mast cell stabilisers in eyes?
Takes time to work need loading dose
What is shown?

Pappiloedema blurred disc
Non proliferative severe retinopathy no macula oedema?
If proliferative?
Consider Photocoagulation (laser)
urgently do if proliferative or very high risk
Risks for corneal ulcers?
Contact lense wear and overnight wear
Immune compromise
What is this?
What grade or hypertensive retinopathy has this?

Grade iv pappiloedema
What is shown? firstline treatment?
What makes this the diagnosis rather than another similar?

Stye- warm compress unless associated conjunctivitis
Likely to be painful wheras chalazion is nto and not inflamed also a stye not blepharitis because it features a small area that is white and bulging
What investigation will find a cataract?
Slit lamp examination, normal fundus and optic nerve seen on ophthalmoscopy
Features of acute glaucoma?
Severe pain- occular and or headache
Reduced visual acuity
Symptoms worse with mydriasis dilation(big word)
Semi dilated pupil (non reactive), halos around lights
Syetmic upset- unwell nausea
Hazy cornea- red eye
Eyelids burn, itch, and stick together.
Symptoms are worse in the mornings.
Both eyes are affected.
Symptoms come and go and flare?
Blepharitis
Proliferative vs non proliferative retinopathy?
comparison shown

Complications of cataract surgery?
Poterior capsule opacification, retinal detachment, inflammation of vitreous humour
AV nipping grade of hypertensive retinopathy?
Grade II silver/copper wiring
What is this what may cause it? Symptoms?

Dendritic ulcer often caused by herpes simplex- refer to ophthal and give topical aciclovir
See a defect in red reflex in elderly adult think?
Cataract as light can not reach retina
What has happened here?

Old laser burns from treatment of diabetic retinopathy (proliferative)
How to perform an RAPD test?
Swing lgiht from eye to eye, eye with problem will consistently start dilating whne light is shone on it and signifies a problem on that side with optic nerve
Initial treatment acute glaucoma?
Beta blockers (caution asthma) and steroids applied topically and pilocarpine (constrict pupil)
IV acetazolomide is used (caution sickle cell)
Surgery: peripheral iridotomy
Offer analgesia and antiemtic also
Non proliferative non-severe retinopathy and no macula oedema?
Observe
Most common blindness cause 35-65 years?
Diabetic retinopathy
Causes of cataract?
Smoking, alcohol, diebetes, trauma, steroids
What is this? best treatment?

Cataract- surgery
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
Blurred vision.
Fluctuating vision.
Impaired color vision.
Conservative management of cataracts?
Stronger lenses.glasses, brighter lighting, does not slow progression, only improves vision for a while
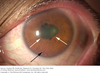
What is shown? ?causes and treatment

Corneal ulcer focal staning with fluorescein
Give antibiotics, often gent and a quinolone
Commonly staph or pseudomonas