Orthopaedics Flashcards
(93 cards)
X ray features of Rheumatoid arthritis
LESS - Loss of joint spaces - Erosions - Soft bones (osteopenia) - Soft tissue swelling
DDx symptoms and signs of RhA vs OA

DDx investigations of RhA vs OA

Tx of RhA
Acute flare
- Corticosteroids
- +/- NSAIDs
Conservative
- PT/OT
- Splints
Medical
- DMARDs (Methotrexate, Sulphasalazine, Hydroxycholoquine)
- Biologics (Infliximab)
Surgical
- Arthrodesis
- Arthroplasty
- Carpal tunnel decompression
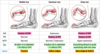
Gout vs Pseudogout
(crystals, shape, Ix, Joint)

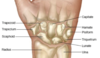
Carpal bones
Some Lovers Try Positions That They Cannot Handle
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrium
Pisiform
Trapizium
Trapizoid
Cuneate
Hamate
Spondyloarthropathies
(PEAR)
Psoriatic arthritis
Enteropathic arthritis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Reactive arthritis
X-ray changes in Ankylosing Spondylitis
X-ray (Pelvis)
Sacroillitis
X-ray (Spine)
Squaring of Vertebrae
Bamboo spine
Syndesmophytes (calcified outgrowths on ligaments)
CXR: Apical fibrosis
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
X-ray (Pelvis): Sacroillitis (diagnostic)
or MRI showing axial inflammation
Associations with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Associations (As)
Anterior uveitis
Apical pulmonary fibrosis
AV node block
Aortic regurgitation
Achilles tendonitis
Aortitis
May cause dilatation of aortic root –> aortic regurgitation
IgA nephropathy
Amyloidosis
ProstAtitis
Atlanto-axial subluxation
Sx of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Inflammatory back pain
- Early morning back stiffness
- Improves with exercise
- Insidious onset
- Age < 40 years old
- Back pain > 3 months
Loss of lumbar lordosis
Kyphosis
Shober’s test +ve (15cm –> 20cm)
Patrick’s test +ve (indicates sacroillitis)
Inflammatory back pain
Criteria (5)
Inflammatory back pain (umbrella term – 4 out of 5 for diagnosis)
- Early morning back stiffness
-
Improvement of stiffness with exercise
- Better at end of the day
- Insidious onset
- Age at onset < 40 years
- Back pain lasting > 3 months
Tx for Gout and Pseudogout
Acute Gout or Pseudogout
- (1) NSAID
- (2) Colchicine (if NSAID C/I)
Recurrent gout
- (1) Allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor)
- (2) Probenacid (increase renal excretion of uric acid)
- (3) Pegloticase (metabolises uric acid into allantoin)
- Lifestyle changes
DEXA scan T score vs Z score
T score = BMD compared to healthy young reference population
T score is used to define osteoporosis (T score < -2.5)
Z score = BMD compared with age-matched control
Tx for Osteoporosis
Conservative
- Smoking cessation
- Reduce alcohol
Medical
(1) Bisphosphonate (Alendronate) (binds to hydroxapatite)
- S/E: Oesophagitis, Osteonecrosis of jaw, Atypical fractures
- Taken on emptying stomach and sit for at least 30min
(2) Denosumab (RANKL inhibitor –> reduce osteoclast activation)
(3) Teriparatide (recombinant PTH) - osteoblast > osteclasts
Strontium ranelate
SERMs (Tamoxifen) - ER agonist in bone but antagonist in breast
HRT
Fracture assessments tools
FRAX score
QFRACTURE
Associations with Ank Spond
Associations (As)
Anterior uveitis
Apical pulmonary fibrosis
AV node block
Aortic regurgitation
Achilles tendonitis
Aortitis
May cause dilatation of aortic root –> aortic regurgitation
IgA nephropathy
Amyloidosis
ProstAtitis
Atlanto-axial subluxation
Tetrad of Henoch Schonlein purpura
Palpable purpuric rash (on buttocks and extensor surfaces of arms and legs)
Arthralgia / Arthritis
Abdominal pain
Glomerulonephritis
SLE Sx
SOAPBRAINMD
4 for diagnosis
- Serositis (pericarditis)
- Oral ulcers
- ANA +ve / anti-dsDNA +ve
- Photosensitivity
- Blood cell deficiency (low Hb, low WBC, low Plt)
- Renal disorders (Lupus nephritis)
- Arthritis / Arthralgia
- Immunological disorders (other auto-antibodies)
- Neurological disorders (CN palsies)
- Malar rash (spares nasolabial folds)
- Discoid rash
Tx of SLE
Acute
- High dose prednisolone
- IV Cyclophosphamide
Chronic
- Lifestyle advice (avoid sun exposure)
- Skin manifestations –> Hydroxychloroquine
- Arthritis –> NSAIDs
Salter-Harris classification

R shoulder pain
Worse when elevating arm above head
Pain on abduction and internal rotation
No trauma
No deformity
No tenderness
No loss of range of movement
Diagnosis? Treatment?
Supraspinatus tendinopathy
Treatment: Physiotherapy
Managed in community
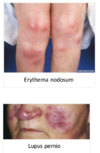
Extra-articular features of RhA

Tx Osteoarthritis
- Conservative
- Modification of ADLs
- Weight loss
- Walking aids
- Physiotherapy / Occupational therapy / Orthotics
- Medical
- Analgesia
- Intra-articular corticosteroids injections
- Surgery
- Arthroplasty (joint replacement)
- Osteotomy
- Arthrodesis