Respiratory Flashcards
(82 cards)
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
TB
Sarcoidosis
Lymphoma
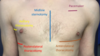
Safe triangle borders
Anterior border of latissimus dorsi
Lateral border of pectoralis major
Line superior to horizontal level of nipple
Apex below axilla
X-ray changes in Heart Failure
ABCDE A – Alveolar oedema (Bat’s wing) B – Kerley B lines (interstitial oedema) C – Cardiomegaly D – Dilated upper lobe vessels (vessels in upper lobe appear bigger than in the lower lobe) E – Pleural effusion
DDx Consolidation
Pneumonia (alveoli with pus)
Malignancy (Alveolar cell carcinoma) (filled with cells)
Lymphoma (filled with lymph)
Pulmonary oedema (filled with fluid)
Pulmonary haemorrhage (filled with blood)
DDx Apical Fibrosis
(APENT)
Aspergillosis / ABPA
Pneumoconiosis (coal, silica)
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
Negative sero-arthropathies (Ank Spond)
TB
DDx Basal Fibrosis
(STAIR)
Sarcoidosis (mid zone)
Toxins (BS NAME)
- Bleomycin, Bulsulfan, Amiodarone, Nitrofurantoin, Sulfaasalazine, Methotrexate
Asbestosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Rheum (Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, SS, Sjogren’s, PM/DM)
T1RF vs T2RF (ABG findings, Pathogenesis, Aetiology, Tx)

Severity of Asthma

Definition of bronchodilator reversibility
Increase in FEV1 > 200ml or 12% of pre-test value
Diagnostic criteria for Asthma (in adults)
Symptomatic
AND
(1) +ve bronchodilator reversbility AND peak flow variability > 20%
(2) Based on FeNO levels AND (bronchodilator or peak flow variability)
Tx of acute asthma attack
Oxygen
Salbutamol (neb)
Hydrocortisone (IV)
Ipratropium Bromide (neb)
Magnesium Sulphate (IV)
Aminophylline (IV)
Ventilation
Long term Asthma treatment for Adults
(1) SABA
(2) SABA + ICS
(3) SABA + ICS + LTRA
(4) SABA + ICS + LABA
(5) SABA + MART (Low)
(6) SABA + MART (Moderate)
(7) Specialist
- Muscarinic receptor antagonist
- Theophylline
- High dose ICS
- Oral prednisolone
Spirometry: Obstructive vs Restrictive (FEV1, FVC, FEV1:FVC ratio)
Obstructive
- ↓↓ FEV1 (<80% predicted)
- ↓ FVC (but decreases by a lesser extent)
- FEV1:FVC < 70% (predicted)
Restrictive
- ↓ FEV1 (<80% predicted)
- ↓ FVC (<80% predicted)
- <-> FEV1:FVC ratio (>70%)
Definition of COPD
COPD = Chronic bronchitis + Emphysema
Characterised by progressively worsening irreversible airway obstruction (i.e. not fully reversible)
Chronic bronchitis = productive cough + mucus hypersecretion on most days for >3 months per year over consecutive years
Emphysema = permanent alveolar wall destruction, resulting in airway collapse and air trapping [histological diagnosis]
Small airways disease = fibrosis of the bronchiole (+ loss of alveolar attachments that hold airway open, not found in Asthma)
Diagnosis of COPD
Post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio < 0.70
(i.e. not reversible obstruction)
Staging system for COPD
GOLD staging system for COPD (based on FEV1)
Stage 1: > 80%
Stage 2: 50-80%
Stage 3: 30-50%
Stage 4: < 30%
Features of exacerbation of COPD
Triad = Increase in SOB, Sputum volume and sputum purulence
Signs of respiatory distress
Examination findings in COPD
Inspection: signs of respiratory distress, pursed lip breathing (increase PEEP)
Palpation: symmetrically reduced chest expansion, reduced cricosternal distance, apex beat not palpable
Percussion: Hyper-resonance
Auscultation: reduced breath sounds, wheeze, coarse crackes
Tx of acute exacerbation of COPD
OSHINIVA (Oxygen, Salbutamol, Hydrocortisone, Ipratropium, NIV, ABx)
Controlled oxygen
- Via 28% Venturi mask
Nebuliser
- Nebulised Salbutamol
- or Nebulised Ipratropium
Steroids
- Oral Prednisolone or IV Hydrocortisone
Non-invasive ventilation
- BiPAP
+/- Antibiotics (if infective exacerbation)
Inhaler Tx of COPD
(1) 1 drug = SABA
(2) 2 drugs = SABA + (LABA or LAMA)
(3) 3 drugs = SABA + (LABA/ICS or LABA/LAMA)
(4) 4 drugs = SABA + LABA/LAMA/ICS

Long term Tx of COPD
Conservative
- Smoking cessation
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Vaccination
Medical
-
Inhaler therapy
- SABA
- SAMA
- LABA
- LAMA
- ICS
- +/- Long term Oxygen therapy (LTOT)
- +/- Mucolytics
-
Rescue pack
- +/- Oral Antibiotics
- +/- Oral corticosteroids
Surgical
- Manage pneumothoraces
- Bullectomy
- Lung volume reduction surgery
- Lung transplant
Bronchiectasis - causes
Post-infectious (most common)
Cystic fibrosis
alpha-1 antitypsin deficiency
Kartagener’s syndrome (bronchietasis, sinusitis, situs invertus)
Yellow-nail syndrome (bronchiectasis, yellow nails, pleural effusion)
Bronchiectasis - Sx
Productive cough with sputum
Fever
SOB
Wheeze
Coase crackles
Clubbing
Bronchiectasis - Ix (best)
HR-CT
- Tramtrack sign / opacities
- Signet ring sign
- Dilated bronchi
- Mucus plugs
- Lung collapse
- Fibrosis