Paper1-SC8 Flashcards
(34 cards)
Explain the core practical on prepariing copper sulfate.

What is a precipitation reaction?
One in which soluble substances in solutions cause an insoluble precipitate to form.
What is oxidation?
Loss of electrons.
How can you obtain a dry soluble salt?
From cystalisation, it is important to have a neutral solution before evaporating the water otherwise you will contaminate the salt with an excess of one reactant. This can be done with titration.
What happens during neutralisation?
Hydrogen ions in the acid combine with oxide ions to form water.
What does metal+acid form?
Salt and hydrogen. Effervescence is seen as hydrogen gas bubbles.
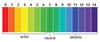
Explain the pH scale.
7 neutral, 14 alkaline and 0 acidic.
What does carbonate+acid form?
Salt+water+carbon dioxide. Bubbles of carbon dioxide are produced and the solid metal carbonate disapears.
What are the main solubility rules?

How can we prepare an insoluble salt?

Explain how the pH scale goes up.
Concentration of h+ ions goes up by 10 time each time the number goes down by one from 7 and below.
What is the equation for concentration?
amount dissolved/volume of solution
Why is an excess of thr base added when preparing soluble salts?
To make sure all the acid is used up.
What do ionic equations show?
They remove spectator ions and only shows ions that change.
How can we predict whether a precipitate will be formed?
We can check the solubility of the products, if both are soluble no precipitate will form.
Explain the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions and what they cause.

What happens to the ions from acids and alkalis during neutralisation?
Hydrogen ions from the acid reaxt with the hydroxide ions and form water. The other ions stay in the solution as ions of the dissolved salt.
Explain some other parts of titration.

What is a soluble base?
An alkali.
How are the salts produced.
By replacing the hydrogen ions with metal ions.
What is the test for carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide turns limewater milky. A lighted wooden splint goes out in a test tube of carbon dioxide but this happens with other gases, too. So the limewater test is a better choice.
Describe the universal indicator pH scale.
Explain the core practical on investigating neutralisation.






