Part 2: Eye Muscles Flashcards
(22 cards)
Levator Palpebrae Superioris function:
Elevation of the upper eyelid
Superior Rectus function:
Elevation and adduction of eye

Inferior Oblique function:
Elevation and abduction of eye

Inferior Rectus function:
Depression and adduction of eye

Superior Oblique function:
Depression and abduction of eye
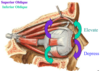
Lateral Rectus function:
Abduction of eye
Medial Rectus function:
Adduction of eye
The only extraocular muscle not attached to the eyeball:
levator palpebrae superioris
attached to upper eyelid
The four extraocular muscles with origins on the common ring tendon:
SOMETIMES I LIKE MILK
- superior rectus
- inferior rectus
- lateral rectus
- medial rectus

Where do the four rectus extraocular muscles insert on the eyeball?
anterior half
Where do the two oblique extraocular muscles attach to the eyeball?
posterior half
The tendon of what muscle passes through a fibrocartilaginous pulley, the trochlea, before turning to reach the back of the eyeball?
superior oblique

The lateral rectus is innervated by:
abducens nerve (VI).
The superior oblique is innervated by:
trochlear nerve (IV).
Muscles innervated by the oculomotor nerve (III):
Some indian men love iguanas.
- superior rectus
- inferior rectus
- medial rectus
- ½ levator palpebrae superioris
- inferior oblique
The two types of muscle in levator palpebrae superioris and their nervous innervations:
- Skeletal muscle (CN3; oculomotor)
- Smooth muscle (sympathetic nerves)
What lesions can result in ptosis (drooping of the eyelid)?
- CN III lesion or a sympathetic lesion
- affects levator palpebrae superioris
Muscles involved in pure elevation of the eyeball:
- superior rectus and inferior oblique contract together
Muscles involved in pure depression of the eyeball:
- inferior rectus and superior oblique contract together
The superior and inferior rectus muscles may be tested by asking the patient to:
- elevate and depress eye from ABducted position.

The superior and inferior oblique muscles may be tested by asking the patient to:
- depress and elevate eye from ADDucted position.

You can test all of the extraocular muscle functions by having the patient’s eyes follow the shape of:
a capital H


