Patho Final Flashcards
(110 cards)
What is cholelithiasis?
Formation of the gallbladder stones dt cholesterol or concentrated pigments
What is cholecystitis?
Inflammation of the gallbladder dt irritation of concentrated bile.
Can cause cholelithiasis
What is choledocholithiasis?
Presence of gallstones in the common bile duct
What is cholangitis? What conditions can cause cholangitis?
Inflammation of the common bile duct.
Maybe dt crohns or ulcerative colitis
What is the normal volume held in the GB?
50-70mls
What does the presence of >70mls of bile in GB mean?
Walls are failing to contract or gallstones are pressent
What is the relationship of calcium with the presence of gallstones
When Ca salts decrease, bile becomes sludgy and the cholesterol can precipitate and form stones
What is bile composed of?
Bile pigments (bilirubin), cholesterol, calcium salts and H2O
What are yellow stones?
aka cholesterol stones. Dt poor lipid metabolism dt obesity or pregnancy. Most common sort. 75-80% of cases
Most often occurs in young females, multiparous, first nations
What are black stones from? Who are most often affected?
Result from excess bilirubin that is stagnant (aka polybilirubin stones).
Most often occurs in hemolytic anemias - sickle cells in africans, enlarged spleen causing increased RBC breakdown
What are brown stones?
combination of of black yellow. Has more cholesterol than black stones but less ca salts than yellow salts
Dt infections of bile duct. Happens in asian descent.
What is the normal color of the gall bladder? What color is it with cholesterol deposits? What color is the GB in chronic cholecystitis with pigmentary stones?
- Normal: green
- Yellow
- Pink - no bile, red areas of hyperemia
What are complications of gallstones?
- Pain
- Inflammation dt stone in mucosa which leads to ulceration and potential fistula formation. Chronic inflammation may also lead to carcinoma
- Obstruction leading to malabsorption

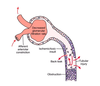
What is the pathogenesis biliary reflux?
- GB contracts
- Bile is sent down the CBD
- Blockage occures in ampulla of Vater, bile cannot enter duodenum
- Bile in pancrease disrupts tissue, digestive enzymes are activated and causes pain
- Bile goes up pancreatic duct

What are S&S of secondary obstruction>
Jaundice, increased conjugated bilirubin levels
WHat is a complication of pancreatic duct obstruction?
When CCK is released the gall bladder contracts. Bile enters the pancreas causing the worst imaginable pain possible in RUQ. The pancreas begins to digest itself dt back up of enzymes.
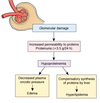
How are cholestasis and intrahepatic biliary disorders related?
- Bile flow in the liver slows down dt obstruction in the bile canalucii
- Bile accumulates and forms blugs in the ducts
- Ducts rupture and damage liver cells. Liver enzymes such as ALT, AST and ATP are released into blood.
- Liver is unable to continue to process bilirubin - causes unconjugated jaundice
- Increased bile acids in blood and skin - causes pruritis
What is primary biliary cirrhosis?
Autoimmune disease causing neutrophils in intrahepatic bile duct.
Neutrophils release inflam mediators which cause the duct wall to thicken, which shuts down the duct, decreasing bile release, causing back up in the liver, causing liver damage
affects women 9:1
Who does primary biliary cirrhosis usually affect?
Women - 9:1
What are diseases of extrahepatic bile ducts?
ie primary sclerosis cholangitis. Segmental. Inflammationof sections causes bile to accumulate which causes stone formation
Usually secondary to a disease like ulcertaive sclerosis or crohns
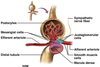
What spinal level are the kidneys at? Which is higher?
Lt kidney is higher than right, found T12 - L3
What is the function of peri-renal fat?
- Holds kidney in place, prevents prolapse
- Protects kidney from truama
- Energy storage
Why is a lack of peri-renal fat in anorexic patients a problem?
Kidneys aren’t held in position by peri-renal fat. Kidneys decsend lower than T12/L1. Increases pressure on the renal artery and vein which decreases the blood flow. May lead to ischemia
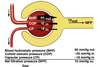
How much does a kidney weigh? How much cardiac output does it receive? How much more is this than it is entitled to by mass?
Weighs 160 g each
Receives 22% CO
55% more than it is entitled to by weight