Pathology of the stomach Flashcards
(32 cards)
What does the normal stomach look like

What are the inflammatory disorders of the Stomach
- Acute gastritis - irritant chamical injury, severe burns, shock, truama or head injury
- Chronic gastritis - autoimmune, Bacterial or chemical
- Rare: lymphocytic, Eosinophillic and granulomatous gastritis
What are the types of chronic gastritis
- Chemical
- Bacterial - H.pylori
- Autoimmune
Describe chronic gastritis
- Rarest
- Leads to production of anti-parieral cells and anti-intrinsic factor antibodies
- causes decreased acid secretion
- Features: Atrophy, Intestinal metaplasia (mucosa looks like intestinal)
- Perinicoius anaemia = decrease in RBC production due to lack of B12
- Macrolytic anaemia = Big RBC due to B12 deficiency
- SACDC - degeneration of posterior and lacteral spincal cord columns - B12 deficiency
What are the features of autoimmune chronic gastritis
- causes decreased acid secretion
- Atrophy, Intestinal metaplasia (mucosa looks like intestinal)
- Perinicoius anaemia = decrease in RBC production due to lack of B12
- Macrolytic anaemia = Big RBC due to B12 deficiency
- SACDC - degeneration of posterior and lacteral spincal cord columns - B12 deficiency

Describe H.pylori Chronic gastritis
- Most common type of chronic gastritis
- Bactiria forms a niche between epthelial cell surface and mucous barrier
- Gram negative curilinear rod
- Exites early acute inflammatory responce - if not cleared then will be followed bt chronic active inflammation
- Site effected: Antrum
What is the key inflammatory element that plays a role in h.pylori gastritis
IL-8 - chemotaxin allows infirtraltion of other immune cells to clear an infection (mice diffiecient cannot clear infection)
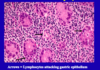
What are the histological features of H.pylori gastritis
- Lamina propria = anti-hp antibodies
- increased risk of doudenal and stomach ulcers
- increased risk of gastric carcinoma and lymphoma
- Infirtration of lymphocytes and plasma cells
- Blue curved bacteria

What does infiltration of lymphocytes look like on histology

Descibe chemical gastritis
- Chronic inflammation due to NSAIDS, alcohol, bile reflux
- Direct injury to mucusal layer by fat solvents
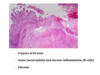
What are the features of chemical gastritis
- Epithelial regeneration, hyperplasia and congestion - as toxin injury causes degredation of cells - back diffusion of gastric acid
- May produce ulcers
- Gastric mucousa = hyperplastic with long foveoles
- Lamina propria = edematous
- Spindle shaped sm cells

Describe chornic doudenal ulcers
- Increased attack by pepsin+acid and failure of defence
- increased acid secretion
- excess acid = gastric metaplasia, H.pylori infection, inflammation, epithelial damage and ulceration
Describe peptic ulcers
- acid secretion and failure of defence
- Morphology = 2-10cm across, clear,cut and punched out

What are the microscopic changes in peptic ulcers
- muscle replaced by fibrous tissue
- Hyperplasia of adjacent lymph nodes
- Distal mucosa has a ladder like configurarion
- Serosal fibrosis
What does a peptic ulcer look like
- layered appearance
- Floor is dicrotic fibronopurulent dibris
- Base is inflamed grannulation tissue
- Deepest layer is fibrotic scar tissue
- Acute neutrophilic and chronic inflammation - B cells

What are complications of peptic ulcers
- Perforation
- Penetration
- Haemorrhage
- Stenosis
- Pain!
What are the type of Binign gastric polyps
- Hyperplastic polyps
- Cystic fundic gland polyps
What are the types of malignant gastric tumours
- Carcinomas - Adenocarcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Describe Gastric adenocarcinoma
- Common in japana, china and promixal tumour of cardia are increasing whilst distal gastric tumours are decreasing
What is the pathogenesis of gastric adenocarcionma
- H.pylori infection - stronge link to distal distal gastric cancers - Type 1 carcinogen
- HP -> Chronic gastritis -> Intestinal metaplasia/atrophy -> Dysplasia -> carcinoma

What are other causes of gastric adenocarcinoma
Pre-malignant conditions
- Perinicious anaemia
- Partial gastrectomy
- HNPCC/Lynch syndrome (hereditory nonpolyp colorectal cancer)
- Menetrier’s disease
What are the subtypes of Gastric adenocarcinoma
- Intestinal type - exophytic/polyploid mass
- Diffuse type- expands/infiltrates stomach wall
What is the intestinal type - adenocarcinoma
- Well-formed glandular strutures
- Polypoid or ulcerating lesions - heaped-up, rolled edges
- Surrounding mucosa has intestinal metaplasia with H.pylori
- Distal sotmach - patients with chronic gastritic
- Strong environmental assoication
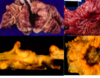
What is the diffuse type - adenocarnoma
- poorly differentiated cells - infiltrate stomach wall
- Can be any part of stomach - eps cardia
- Worse prognosis compared to intestinal type
- Loss expression of E-cadherin molecules - key event in carcinogesis