Pattern Recognition Flashcards
(309 cards)
What are the 4 components of a medical image?
Equipment Patient Signal Receptors Signal Processing
Describe equipment as a component of a medical image.
It is dealt with in relation to the patient It relates to: - positioning of equipment - equipment used - MRI specific or surface coils
Describe signal processing as a component of a medical image
It tended to via a computer using specific algorithms Can be chemical in terms of film processing
Describe signal receptors as a component of a medical image
Change between modalities - Transducers - Image recording plate - Film / Screen combination - Radioreceiver - PMTs
Describe the patient as a component of a medical image
Need to understand the anatomy and physiology Positioning of the patient
What needs to be understood to interpret an image?
- Interaction of the source with various tissue types - Affect of beam geometry - Affect of patient position on structures - Anatomical structures (localisation, physiology and manifestation of disease)
What is the effect of beam divergence? How is it reduced?
Image magnification Gives a geometric unsharpness Reduce by placing the recording medium as close to the object
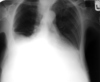
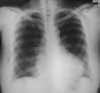
Why is a chest X-ray taken PA?
Allows for assessment of heart size It reduces unsharpness and magnification It reduces the effect of breast tissue If AP then the scapula can be projected into the lung field
How is a chest X-ray taken?
PA (posterio-anteriorly) Remove the scapula out of the image view
How does shade and colour alter perception of images?
Shade helps to identify structures The mind fills the gap to create the perception of depth 10% of colour interpretation is governed by context not wavelength
What are the problems associated with radiography?
3D representation in a 2D image Summation of shadows Standardisation in positioning is vital to identify positioning and location
What is the benefit of standardisation of positioning?
Allows you to identify the position and the location You become familiar with the orientation - familiar frame of reference
How are hands X-rays usually acquired?
Dorsi-palmar Need to label right and left
What is a reason for altering from a standard projection?
Makes it more comfortable for the patient If the patient is less likely to move
What are the 4 different types of contrast?
Subject Recording medium/system - Image Objective Subjective
What is the difference between subject and image contrast?
Subject contrast is the differences between X-ray intensities emerging from the patient Image contrast is the differences recorded in the radiographic image
What is the difference between subjective and objective contrast?
Subjective - dependent on the eye of the observer, varies from person to person Objective - actual differences in densities or black and white
How can subject contrast be changed?
Altering differences in attenuation using contrast agent - Barium, iodide, gadolinium
What are examples of contrast agent?
Barium Iodide Gadolinium
What are examples of contrast agent?
Barium Iodide Gadolinium
Why is it important to get the patient, X-ray detector and beam source parallel?
Need to get a truly representative image Otherwise can get: foreshortening or elongation
What is foreshortening in an X-ray image?
The image appears squashed Happens when the patient leans forward
What is elongation in an X-ray image?
If the detector is angled you get a stretched/elongated image Can be used advantageously in the scaphoid
Where can beam geometry be applied usefully?
- PA chest radiography - Sacroiliac joints demonstration - Aid to identifying patient positioning