pharmacology 2 Flashcards
(51 cards)
How are drug effects quantified? And how is this relationship described?
By studying the relationship between drug concentration (or dose) and the response produced by the drug.
This relationship is described by concentration-response curves.

What are the three main types of pharmacological experiments?
In vitro
In vivo
Ex vivo
Experiments in vitro - how are the drug effects studied?
On a piece of tissue dissected from an animal (or human) and kept alive outside the body
This is by far the most common type of experiment
Includes experiments on cells grown in tissue culture.
Experiments in vitro - what are the responses that might be measured?
Changes in tension of a muscle
Changes in the activity of an enzyme
Changes in the secretion of a hormone or neurotransmitter
In vivo experiments- how are the drug effects studied?
In the living animal (or human)
Include clinical trials
Tightly regulated by the Home office in the UK
In vivo experiements - what are the responses that might be measured?
Increase in blood pressure
Reduction in pain threshold
Reduction in allergen-induced bronchoconstriction
Ex vivo experiments- how are the drug effects studied?
A tissue or organ is removed from an animal that has been treated with a drug
The effects the drug has had on organ function are tested in vitro
This is also very tightly regulated by the Home Office
Examples of ex vivo experiments
Examples might include experiments to see whether longterm treatment with a drug induces liver damage or alters some aspect of brain biochemistry
(log) concentration- response curve- the concentration axis
Invitro= concentrations are expressed in Moles per litre I.e Molar (M)
1 mole of a drug contains 6.02 x 10^23 drug molecules and weighs the molecular mass, in grams
A 1 Molar solution contains 1 Mole of a drug dissolved in 1 litre of solvent
Most importantly, a 1 Molar solution of a drug “X” will contain the same number of drug molecules as a 1 Molar solution of drug “Y”
What suggests a drug is clinically useful?
It acts at a very low concentrations.
At what concentration range do most drugs act at?
Most drugs act at concentrations in the range 1 x 10-6M to 1 x 10-12M i.e. they are very potent (see later)
How many drug molecules per litre does a 10-9 M solution of drug contain?
Bear in mind however that a 10-9 M solution of drug still contains 6.02 x 1014 or 602000000000000 drug molecules per litre!
Often pharmacologists will use the prefixes milli (m)- micro () - and nano (n)- for 10-3 ,10-6 , and 10-9 respectively. How to convert between them?
……
thus 1 micromolar (M) solution is the same as a 1 x 10-6 M solution
Constructing a concentration-response curve

Constructing a concentration- response curve

Constructing a cumulative concentration-response curve
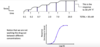
Doses in vivo - why is it not possible to use molar concentrations? How are drug doses expressed?
Because the volume of the solvent (e.g blood) is not known
As weight of drug per weight of animal e.g 1mg per kg (1mgkg-1)
This allows an approximate extrapolation of the dose from, for example, a 20-gram mouse to a 70 kg human.
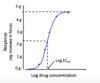
(log) concentration-response curve- what is the maximum effect (Emax)?
Indicates the maximum response (effect) the drug can produce
It is the top of the curve, where increasing the concentration of the drug produces no greater effect.

(log) concentration- response curve- What is the EC50?
Tells us the position of the curve on the concentration axis.
Defined as “the Molar concentration of a drug that produces 50% of the maximum response for that drug”
Sometimes use other percentage values such as EC90 or EC20
What is potency?
What is a potent drug?
A drug that is effective in very small amounts
What does a lower EC50 mean for the potency of a drug?
Lower EC50 value means the drug is more potent.
How to calculate the relative potencies of two drugs with the same action ?
- Compare their EC50 values described by the potency ratio (M)
- Often we will be comparing a new drug (the test drug) with a drug that is already available (the standard drug)
M and log M equations
M = EC50(test)/EC50(standard)
log M = logEC50(test) – logEC50(standard)




