Pharmacology and Therapeutics - Fletcher Flashcards
(32 cards)
What are the 5 key functions of the kidney?
Hydroxylation of Vitamin D
Excretion of waste products
Excretion of salt and water
Red blood cell production
Control of blood pressure

What is an AKI?
And what chemcial changes occur due to it?
Acute Kidney Injury
A sudden reduction in kidney function over hours or days, unsually with no symptoms
Usually causes a rise in serum creatinine and reduction in urine output

What are the 3 categories of causes of AKIs?
Pre-Renal –> Reduced blood supply, sepsis (causes drop in BP) or shock
This is the most common
Intrinsic –> Problem with the kidney itself (eg, drugs and inflammation)
Post-Renal –> An outflow obstruction (such as the bladder/ureter or prostate)

What are the 2 key risks in the community for AKIs?
Dehydration (potentially N+V)
Nephrotoxic drugs (like NSAIDs)

Why are NSAIDs, ARBs and ACEi problematic in AKI?
NSAIDs –> Act on prostaglandins, preventing vasodilation at the afferent arteriole
ARBs/ACEi –> Both act on angiotensin II, which therefore prevents vasoconstriction at the efferent arteriole
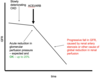
When is Contrast Media contraindicated?
In AKI grade 2 and 3

What are sick day cards?
Advice on what to do if you are acutly unwell (eg, diarrhoea and vomiting) to ensure that an AKI doesnt occur
Things include stopping certain medications, and keeping hydrating

What are the conditions needed for VTE prophylaxis in medical and surgical patients?
Medical –> Have had or are expected to have reduced mobility for 3 or more days
Surgical –> Most patients will need anticoagulation
Total anasthetic and surgery time is over 90 mins, or 60 mins for lower limb surgery

What is the duration of VTE Prophylaxis for certain surgical procedures?
NOF –> 4-5 weeks
Abdominal/Pelvic Cancer –> 4 weeks
Lower limb in plaster –> Until out of the plaster
Hip/Knee Replacement –> DOAC used for prologed period of time

What’s an epidural?
When an anasthetic and an opioid is injected into the epidural space, which paralyses the area
There’s a risk of epidural haematoma when inserting or removing the epidural catheter in an anticoagulanted patient
What are the 4 parts of the APFEL score?
Female = 1
History of PONV = 1
Non Smoker = 1
Opiate Use = 1

Can you or can you not use metaclopramide in PONV?
It is not very effective!!
What are the 3 types of Surgical Site Infections (SSIs)?
Superficial
Deep Incisional
Organ/Space

What are the 4 degrees of contamination during surgery?
Clean –> The respiratory and genitouretary tracts arent enetered and no inflammation is encountered. No break in aspetic technique
Clean-Contaminated –> The respiratory or genitouretary tracts are entered, but with minimal spillage
Contaminated –> Operations where inflammation (without pus) is encountered, or there is visible contamination of the wound
Dirty –> Operations in the presence of pus or compound injuries more than 4 hours old

On a surgical ward, when would a pharmacist do a medicines reconcilliation/screen the drug chart?
On the day of the surgery BEFORE sedative meds are given to ensure that the patient can be a more useful source
What are the 3 different methods of prophylaxis of VTE?
Actions –> Avoid dehydration, and stop medication which could cause problems. Also useful to get people mobilised quickly after surgery
Mechanical –> Stockings, IPCs and Foot impulse devices
Pharmacological –> LMWH, heparin, DOACs, fondupariux

What types of medication do we need to be careful with pre-surgery?
Anticoagulants/Anti-platelets
Cardiac drugs
Steroids
Hyperglycaemics
Oral contraceptives
Tamoxifen
MAOIs
Lithium
What is the prophylactic dose and treatment dose of dalteparin?
Prophylaxis –> 5000units OD
Treatment –> 15,000units OD
When would we not restart wafarin ASAP after surgery?
If the bleeding risk is high
If an epidural is in situ
What are the reveral agents for wafarin and for DOACs?
Wafarin –> Vitamin K (slow reveral) and Beriplex (1 hour reversal)
DOACs –> Idarucizumab (for dabigatran only/very expensive) for life threatening emergencies
What type of cardiac medication is always continued in surgery?
Beta-Blockers
This is because of the risk of rebound tachycardia and arrhythmias
What is the dose of hydrocortisone IV for minor and major surgeries?
Minor –> 25-50mg on induction
Major –> Usual steroid dose in the morning plus 25-50mg on induction
Also 25-50mg TDS for 48-72hrs post op (24 for moderate surgery)

When would a Various Rate Intravenous Insulin Infusion (VRIII) be indicated?
When more than one meal has been missed (in major surgery)
When there is uncontrollable hyperglycemaia in a patient that has missed only one meal
What type of oral contraceptive can increase the VTE risk of a patient?
Oestrogen containing pills
Progesterone only pills cause no increases risk






