Pictures Flashcards
(31 cards)
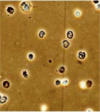
What is shown here?
renal cortex
note the glomeruli everywhere
also DCT & PCT will be prevalent. PCT will be the ones w/ the fuzzy lumen.
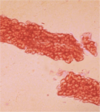
What’s this?

glomerulus
not the endothelium & PCT (fuzzy) etc.
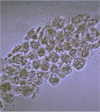
What is this?

glomerulus
E: endothelium
F: fenestration
C: capillary
BM: basement membrane
P2: secondary podocyte process
FS: filtration slit
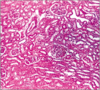
What is shown here? What’s the big black glob in the middle?
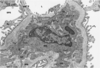
another glomerulus
big black glob is the nuclei of the mesangial cells. Lays down matrix in the middle there.
What is this?

PCT. can tell b/c of the brush border of microvilli for increased absorption. found in the cortex.
What’s the difference here b/w the DCT & PCT?

DCT smooth w/o microvilli of brush border.
What’s this?
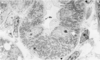
PCT
see the microvilli!
What is the function of the cell marked J?

juxtraglomerular cells
secrete renin if they sense decreased renal blood flow b/c they assume–our systemic BP is too low! Let me fix that!
What is this?
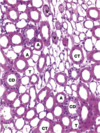
renal medulla
not cortex b/c you can’t see glomeruli
see arteries, veins, collecting tubules & ducts
note: vasa recta is found here!
What is the thing labeled DB, PCS, U? What type of epithelium is found here?
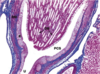
uroepithelium!
DB: ducts of bellini
PCS: pelvicalyceal system
U: beginning of the ureter
What is the problem here?

hypercellularity following glomerular injury
What is the problem here?

Nothing! It’s normal : )
What is the problem here?

basement membrane thickening as a result of glomerular injury
What’s the problem here?
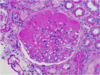
hyalinosis
see some eosinophils, sclerosis, collagen deposition
What’s the problem here?
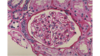
nothing, it’s normal! : )
What’s the problem here?

sclerosis as a result of glomerular injury
What is this?

Immunofluorescence shows granular pattern. Indicative of heymann in situ pattern of glomerular injury. Will also expect to be able to see antigen-antibody complex depositions on the subepithelium on electromicrograph.
What is this?
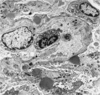
electromicrograph shows complex deposition on subepithelium.
In situ Heymann form of glomerular injury
What does this show?

this shows a linear pattern
consistent with in situ anti-GBM glomerular injury
antibody binds collagen in basement membrane
**won’t be able to see anything on electromicrograph b/c it is so consistent, & not really deposits
What is this?
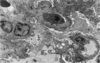
this electromicrograph of the glomerulus is free of any deposits b/c in situ anti-GBM glomerular injury is diffuse binding of antibody to collagen in the basement membrane. doesn’t show up on here.
A 48-year-old man with a history of pyelonephritis presents to the emergency department with fever (38.4° C), nausea, vomiting, and sharp costovertebral pain. He had been diagnosed with pyelonephritis caused by Escherichia coli a month earlier and was treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for two weeks. He is admitted to the hospital. His WBC count is 21,500/mm3 with a left shift. His hematocrit is 32 and he has an elevated ESR. Urinalysis shows leukocyte esterase (+) and nitrite (+). Urine culture grows E. coli, but blood cultures are negative. A CT scan of the left kidney reveals what? Treatment?
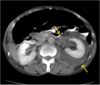
perinephric abscess
drain abscess percutaneously so that antibiotics can reach it.
IV antibiotics, here: ceftriaxone & gentamicin
Those little wispy things are the virulence factors for what? which condition?

Type I Fimbrae for E coli
UTI!! Attaches to uroepithelial cells
What do you see here? What could have caused this if it was related to a UTI?

big kidney stone
staghorn calculi
excess ammonium from proteus mirabilis producing urease
What is this?

this UA shows the color of myoglobinuria
perhaps from rhabdomyolysis