POM derm pics Flashcards
(32 cards)

–Plaques – Large, measure greater than 5mm, often formed by a confluence of papules. i.e. psoriasis

•Cysts – are enclosed cavities with a lining that can contain a liquid or semisolid material. i.e. sebaceous cyst.

•Telangiectasia – is a dilated superficial blood vessel.

•Bullae - are large vesicles (equal to or greater than 6mm). i.e. pemphigus
plaques, cysts, telegiectasia, and bullae are examples of (primary/secondary) lesions
primary
excoriation, lichenification, edema, scale, fissure, erosion, ulceration, atrophy, scar, hypo/hyper/de-pigmentation and crust are examples of (primary/secondary) lesions
secondary
ABCDE staging of nevus stands for
asymmetry, border, color, diameter (greater than 6mm), evolution
what type of carcinoma
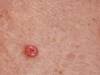
basal cell.
- MC form of skin cancer, usually occurs in sun damaged skin.
- Can cause a lot of local damage, but typically does not metastasize.
- Smooth, round, pearly borders with central pallor or ulcer.
- Recurrent bleeding, failure to heal.
- Tx - excision
what type of cancer

squamous cell.
- 2nd MC form of skin cancer.
- Sun Exposed areas. Can metastasize.
- Ulceration, scabbed over, recurrent bleeding, becomes deeper, ulcerated over time.
Treatment – excision
what type of cancer
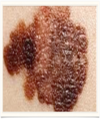
malignant melanoma.
- Lethal form of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes.
- Often seen in non-sun exposed areas.
- Metastasizes early and widely.
- Treatment – need wide excision by a professional (dermatologist or surgeon) if melanoma is suspected.
what type of cancer
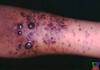
Kaposi Sarcoma.
- Neoplasm of the endothelium and epithelial layer of the skin caused by Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus 8
- Commonly associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
- Treatment – Improves as HIV is treated.
what common abnormality?
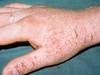
Eczematous Dermatitis -
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Initial Treatment – Avoid offending agent and use topical steroid medication if needed.
what common abnormality?

Rosacea
what common abnormality

folliculitis. •Inflammation of the hair follicle, infected with bacteria, usually staphylococcus
what common abnormality

cellulitis. infection, can be quite severe
what common abnormality

psoraisis.
- Tends to run in families, affects 2-3% of the U.S. Population. Exact cause not known, but thought to be caused by errors in immune system function.
- Can be triggered by emotional stress, skin injury, infection, and certain medications. Plaques improve with sun exposure.
- Thick red, silver-grey patches on extensor surfaces.
- Nail pitting and onycholysis.
what common abnormality

Acanthosis Nigricans.
- Nonspecific reaction pattern most commonly associated with obesity, and diabetes (insulin resistance). Also seen in polycystic ovarian disease, malignancies (rarely), or as an inherited disorder.
- Velvet, leathery thickening of the skin, primarily affects skin folds.
what common abnormality

herpes simplex type 1
what common abnormality

herpes simplex type 2

herpes zoster/shingles.
- Grouped Vesicles on an erythematous base, follow a sensory dermatome
- Varicella virus
- Elderly (over the age of 70), and immunosuppressed 15x more likely to get it.
- Postherpetic neuralgia – 40% of the elderly who get Shingles.

vitiligo. Autoimmune disorder, attacking pigmented cells

alopecia areata. •Sudden, rapid, patchy loss of hair, usually from the scalp or face
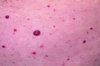
cherry hemangiomas/angiomata.
- Mature capillary proliferations common in middle-aged and older adults.
- No treatment is generally necessary.
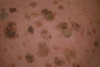
Seborrheic keratoses.
•Common benign, slow growing epidermal tumors due to a benign proliferation of immature keratinocytes.
Well demarcated, typical stuck-on appearance, generally asymptomatic ment–>










