Practical Flashcards
Where do T-cells mature?
Thymus
What are organized regions of the adaptive immune cells that allow for antigen specific immune responses?
Lymphoid follicles
What are clusters of lymphoid follicles in the wall of the distal portion of the small intestine?
Peyer’s Patches
What is the structure labeled A?

Capsule
What is the structure labeled B?

Subcapsullar Sinus
What is the structure labeled C?

Outer Cortex
What is the structure labeled D?

Trabecular Sinus
What is the structure labeled E?

Germinal Center
What is the structure labeled F?

Trabecula
What is the structure labeled G?

Inner cortex
What is the structure labeled H?

Medullary Sinus
What is the structure labeled I?

Medulla
What is the left arrow pointing to?

Cortex
What is the middle arrow pointing to?

Medulla
What is the right arrow pointing to?

Hillum
What is the top arrow pointing to, and what cells are there?
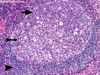
Germinal Center (dark zone)
Proliferating and hypermutating B cells (centroblasts)
What is the middle arrow pointing to, and what cells are there?

Germinal Center (light)
Specified B cells (Centrocytes)
What is the bottom arrow pointing to, and what cells are there?

Mantle
Naive B-cells
What is this?

Hassall’s Corpuscle
What is the top arrow pointing to?

White pulp - lymphoid follicle
What is the bottom arrow pointing to?

Red pulp
What stains dendritic cells?
Fascin
What is positive selection?
Survival dependant on being able to bind to MHC molecule
What is negative selection
Survival dependent on not recognizing self-antigen