Proteins Flashcards
(17 cards)
Proteins are polymers that are also known as…
Polypeptides
Which elements do they contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen, and some proteins contain sulphur
The monomer that repeat to make up the polymer are called…
Amino acids
Amino acids have a general structure of…
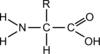
The NH2 group is called…
The middle group is called…
The COOH group is called…
The amino group
The R group (which is different for each amino acid)
The acid (or carboxylic) group
What happens when two amino acids join together?
A condensation reaction occurs, a water molecule is lost and a dipeptide is formed. The bond between the carbon and nitrogen is called the puptide bond
If the reaction is reversed it is called…
A hydrolysis reaction
What is the primary structure of amino acids and which bonds are present?
The primary structure is the amino acid sequence and peptide bonds are present
What is the seconday structure of amino acids?
How the primary structure folds for the first time
What are the two most common secondary structure folds?
A corkscrew-like arrangement called an alpha helix and a uniform zigzag arrangement called beta pleated sheet
How is the secondary structure of amino acids held in place?
By hydrogen bonds which are weak attractions between oxygen and hydrogen atoms in the primary structure
What is the tertiary structure?
The 3D shape that the secondary structure folds into, which is determined by the amino acid sequence
Which three bonds are present in the tertiary structure?
Weak hydrogen bonds, which are easily broken by heat or pH, Ionic bonds, which are stronger and form between R groups, and Disulphide bridges, which are very strong covalent bonds that form between sulphur atoms in the R group of Cysteine
Where is a quaternary structure found?
In proteins which contain more than one polypeptide chain, like in haemoglobin which has four polypeptide chains associated together
What is a prosthetic group?
A non-polypeptide that has been incorporated into a protein’s structure. For example, heme, in haemoglobin contains an iron group. Not all prteins include prosthetic groups
What are the two classifications of the 3D structure of a protein?
Globular proteins, which are used for metabolic processes, and fibrous proteins which are mostly used for structural processes
What is the test for proteins?
The biuret test: add an equal volume of a strong base (such as KOH) to the sample. Add a few drops of copper (II) sulphate solution and mix gently. Colour change from blue to lilac indicates the presence of a protein


