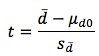Quantitative Methods Flashcards
(129 cards)
Quantitative Methods
Interest Rates
Three ways to interpret interest rates
- Required rate of return
- Discount rate
- Opportunity cost
Quantitative Methods
Interest Rates
3 components of interest rates
- Risk free rate
- Inflation
- Default risk
Quantitative Methods
Interest Rates
Periodic interest rate
Simple rate of interest over a single compounding period
e.g. interest rate of 1.5% per quarter
Quantitative Methods
Interest Rates
Stated annual interest rate
= quoted interest rate
Annual rate ignoring compounding e.g. 4 * quarterly interest rate
Quantitative Methods
Interest Rates
Effective annual rate (EAR)
Annual interest rate taking into account compounding
Quantitative Methods
What is an “annuity due”?
Annuity with first payment at T0 (so last payment at T(n-1)
Formula: FV of annuity

IRR Problems
1 - Reinvestment Problem
2 - Scale Problem
3 - Timing Problem
IRR Problem 1
Reinvestment Problem
Assumes that all cash flows can be reinvested immediately at the IRR rate.
IRR Problem
2 Scale Problem
IRR ignores the scale of the return unlike NPV which would prioritise larger cash returns with the same IRR.
IRR Problem 3
Timing Problem
In the case where two projects have differing cash flow profiles (big cash flows early or late) IRR comparison is not useful.
Definition: Holding Period Return (HPR)
aka Total Return
This is the total return over a given period, including capital and distributions.

Dollar Weighted Rate of Return
Basically the IRR of an investment, taking amount and timing of cash flows into account.
So investing more cash when portfolio value is low leads to positive return, even if portfolio performance over the whole period is unchanged.
Thus a measure of what you earned from investing in the portfolio over the period, not a measure of the performance of the portfolio itself.
Time Weighted Rate of Return
The compound growth rate of $1 invested in the portfolio over the period. Ignores timing of cash flows (ie purchase/sale of portfolio) so is appropriate for measuring portfolio performance.
Simply calculate the return for each period (divs and share price movement) and then annualise.
Money Market Instruments
Bank Discount Yield
Definition and formula
This is the basis on which money market instruments are quoted.
Discount = FV - price you pay
t = Time to maturity

Money Market Instruments
4 money market interest rates
- Holding Period Yield (HPY): simple periodic rate, just discount/FV or (FV-PV)/PV
- Bank Discount Yield: Odd simple annualised rate used for money market, (discount/FV) * (360/t)
- Money Market yield (rm): Simple annualised yield, 360 basis, =HPY * 360 / t
- Effective Annual Yield: Proper compound annual yield, = (1+HPY)365/t - 1
Money Market Instruments
Bank Discount Yield
Issues with them
- Based on the FV instead of purchase price, return should be measured off purchase price
- Annualised of 360 days instead of 365
- Annualised with simple interest, ignores value of compounding
Money Market Instruments
Holding Period Yield
Total return earned if held to maturity (not annualised).

Money Market Instruments
Effective Annual Yield
The annualised HPY based on 365 day year, annualised.

Money Market Instruments
Money Market Yield
aka?
definition
calculation from BDY
a.k.a. CD equivalent yield
Annualised HPY using simple interest on 360 day basis. (HPY = holding period yield).
rmm = HPY * 360 / t
From BDY:

Bonds
Bond Equivalent Yield
Bond yields (in the US) typically quoted semi-annually. This method just doubles it (ignoring compound interest) to get an annualised yield.
So DON’T compare an annual yield bond to the BEY of a semi-annual yield bond.
Statistics
Definition of Parameter
A characteristic (value) of a population (not of a sample), denoted by greek letter.
For example the mean.
In investments, examples inlcude mean return and standard deviation of returns.
Statistics
Definition of a Statistic
An estimate of a parameter of a population, taken from a sample of that population.
Statistics
Definition of Inferential Statistics methods
Required qualities of the sample
Inferential Statistical Methods are used to draw conclusions about a large group based on a sample taken.
Require the sample to be either random or representative in different cases.