Quiz 2 - Lec 9-10 Flashcards
(88 cards)
what is the longest bone in the human body?
femur
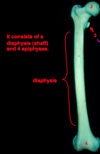
parts of the femur?
diaphysis (shaft)
4 epiphyses (secondary ossificaiton centers that will fuse by the mid-20s
relevant lines/angles in the femur bone?
- line of gravity
- long axis of diaphysis
- angle of oliquity/bicondylar angle (10-15 degrees), which is the normal anatomical orientation of femur during quiet standing/upright

angle of inclination
angle between long axis of head and neck of femur
average is 126º –> less in females due to greater distance between acetabulae (due to wider true pelvis)

how does angle of inclination change as you age?
angle of inclination decreases to 120º (from 126º)

CC: coxa vara
angle of inclination is LESS THAN 120º –> producing stress on femoral neck

CC: coxa valga
angle of inclination: > 135º (normal is 120-135)
Greater than 135º results in INCREASED joint pressure at 180; no skeletal checks restricting ROM –> predisposes to dislocation
Q-angle
q-angle = quadriceps angle
8º angle between ASIS and line of gravity (to midpoint of patella)
CC: genu varum & Q-angle
(bow-legged); tib/fib is towards midline
SMALL OR NEGATIVE Q-ANGLE
CC: genu valgun & Q-angle
knock-kneed; tib/fib away from midline
Q-angle is greater than 17 degrees –> causes undue stress
how to “side” the femur?
- Hold the femur in front of you with the smooth side of the shaft against your fingers and the side with the vertical ridge against your thumb.
- If the head of the femur faces medially and the rough greater trochanter faces laterally and to your right, it is from the right side.
femoral head: characteristics
- Conforms to a spheroidal geometric shape (2/3 of a sphere)
- Nearly all articular, except for the fovea capitis femoris
- Sharply defined border, except anterosuperiorly
- Covered with hyaline cartilage, except in the fovea
- Subject to osteoarthritic disease
femoral neck: shape and orientation
- hourglass in shape
- set obliquely to the shaft (15º anterior to a frontal plane)
- (head and neck are angled away from the surface when placed on flat table –> angle of torsion)
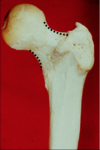
angle of torsion
also called angle of declination
- formed by looking at the relationship between the axis of the femoral head and neck and the femoral condyles

CC: how to treat torsional femur deformities?
subtrochanteric derotational osteotomy

CC: what is a presentation of torosional femur deformities?
Commonly presents as “in-toeing”, because with ABNORMAL FEMORAL NECK ANTEVERSION, the patient will in-toe to place the femur in a better spot in the acetabulum

which torosional femur deformity is associated with IN-TOEING?
(anteversion/retroversion)
femoral neck ANTEVERSION

where does anterior side of femoral neck join the femoral shaft?
intertrochanteric line, which extends from greater to lesser trochanter

iliotrochanteric band: what attaches here?
part of the iliogemoral ligament of hip joint capsule
where does posterior side of femoral neck join the femoral shaft?
intertrochanteric CREST
(more pronounced than the line and found posteriorly)

where does femoral neck end SUPERIORLY?
greater trochanter

where does femoral neck end INFERIORLY?
LESSER trochanter

intertrochanteric line turns posteriorly and becomes….
the spiral line

greater trochanter: functional sides/surfaces
medial surface: concave w/ trochanteric fossa posteriorly
lateral surface: convex w/ ridge line