Quiz 3- Lec 17-19 Flashcards
(58 cards)
important osteology and ligaments
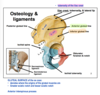
osteology of femur: proximal end
identify: greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity


important ligaments in the gluteal region
- sacrospinous ligament
- sacrotuberous ligament
2 important foramina of gluteal region
(formed by notches and ligaments)
- greater sciatic foramen
- lesser sciatic foramen

major structures that leave the pelvis through:
greater sciatic foramen to enter the gluteal region
- superior and inferior gluteal artery, nerve, vein
- piriformis m
- pudendals (internal pudendal artery & vein, and pudendal nerve)
- sciatic nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous
- nerve to obturator internus
- nerve to quadratus femoris
major structures that leave the gluteal region through:
lesser sciatic foramen to enter the perineum
- pudendals (pudendal nerve, internal pudendal vein & artery)
- nerve to obturator internus
structures that enter gluteal region thru
lesser sciatic foramen
obturator internus tendon
muscles of gluteal region
- GLUTES
- maximus
- medius
- minimus
- tensor fasciae latae
- piriformis
- superior gemellus
- obturator internus
- inferior gemellus
- quadratus femoris
- obturator externus
tensor fasciae latae:
origin, insertion
- o:
- anterior 1/4 of lateral lip of iliac crest lateral side of ASIS &
- interspinous fossa fascia lata & gluteal fascia
- ins: travels b/w 2 layers of fascia lata to insert on IT band (tract)
tensor fasciae latae:
act, inn
- action: abduction, medial rotation, & flexion of hip; assists w/ knee extension; helps to tense fascia lata
- inn: superior gluteal nerve (L4)

gluteus maximus:
origin, insertion
- origin
- ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line
- sacrotuberous ligament
- dorsal surface of distal 2 sacral segments and coccyx
- [aponeurosis of erector spinae, dorsal sacroiliac lig & fascia lata]
- ins
- superior and superficial fibers insert into IT tract
- deep fibers insert into gluteal tuberosity
gluteus maximus:
action, innervation
- action: power extension of hip, raise trunk from flexed position, superior fibers abduct hip, other fibers adduct hip; lateral rotation of hip, tenses fascia lata
- inn: inferior gluteal nerve

gluteus medius:
origin, insertion
- origin:
- ilium between posterior and anterior gluteal lines
- gluteal fascia
- ins
- diagonal ridge of lateral surface of greater trochanter

gluteus medius:
action, innervation
- actions:
- abduction of hip (stabilizes pelvis)
- anterior fibers flex & medially rotate hip
- posterior fibers extend & laterally rotate hip
- innervation: superior gluteal nerve
gluteus minimus:
origin, insertion
- o: ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
- ins: depression on anterior side of greater trochanter

gluteus minimus:
actions, innervation
- actions:
- abduction of hip (also stabilizes pelvis)
- flex and medially rotate hip
- inn: superior gluteal nerve

CC: lurch gait is a symptom of lesion of which nerve?
inferior gluteal nerve
(characterized by posterior leaning of the trunk at heel strike in order to keep hip extended during stance phase.)
combined actions of gluteus medius and minimus….
prevents pelvic tilt/drop on the contralateral side
CC: Trendelenburg gait and sign is a symptom of lesion of which nerve?
lesion of superior gluteal nerve
(When standing on the right leg, if the left hip drops, it’s a positive right Trendelenburg sign (the contralateral side drops because the ipsilateral hip abductors do not stabilize the pelvis to prevent the droop)
piriformis
origin, insertion
- o:
- pelvic surface of sacrum (lateral parts of S2 - S4 segments)
- [ventral sacroiliac & sacrotuberous ligaments]
- ins:
- “tip” of greater trochanter

piriformis:
actions, innervation
- actions:
- laterally rotate hip
- abductor of thigh w/ hip flexed
- innervation: twigs from ventral rami (S1 & S2), nerve to piriformis in pelvis

obturator iNTERNUS & superior & inferior gemelli
origin & insertion
- origin
- Obturator internus: bony internal margin of obturator foramen and obturator membrane
- Superior gemellus: external surface of ischial spine
- Inferior gemellus: superior edge of ischial tuerosity, next to obturator notch
- insertion: all 3 thru combined tendon into medial side of greater trochanter, anterosuperior to trochanteric fossa

obturator INTERNUS, & superior/inferior gemelli
actions, innervation
- actions: all 3 laterally rotate hip and abduct the thigh with hip flexed
- inn:
- Obturator internus & superior gemellus: nerve to obturator internus
- Inferior gemellus (and quadratus femoris): nerve to quadratus femoris
quadratus femoris:
origin, insertion
o: lateral side of ischial tuberosity and from part of body of ischium
ins: quadrate tubercle and bone inferior to it