radiographic findings Flashcards
(34 cards)
occipitalization
basilar impression and c2-3 blocked vert often seen with
agenesis of the posterior arch

-post arch doesnt fuse -fibrous ct -no post arch -C2 megaspinous
kimerle’s anomaly

posterior ponticus/arcuate foramen
Barre-Lieou syndrome
-posterior ponticus -headaches, retro orbital pain, vision changes, problems swallowing, speech problems
os terminale persistans of bergmann

-downs -non fusion at dens, usually fuses at 12-13
os odontoidium

-dens doesn’t fuse -4 or more mm of translation between flex/ext -contraindicated
congenital block is associated with?
- usually cervical or t12-L5 -wasp waist presentation
- aka failure of segmentation
surgical block
no anterior body concavity (wasp waist) no posterior arch fusion
klippel-feil syndrome

- multiple block vert -hemi -short webbed neck, low hairline, limited ROM
- renal anomalies in 35% -sprengel’s deformity (undescended scapula)
- omovertebral bone

omovertebral bone

from posterior arch to superior angle of scapula, often seen with sprengels
cervical spondylolisthesis

-congenital defect in post arch -1-3 mm anterolisthesis
cervical rib

-66% bilateral -may cause TOS -must have an articulation otherwise just elongated tp
butterfly vertebra
-hemi that is narrower in the middle
incarcerated hemivertebra
when the adjoining segments are configured to accommodate the hemi
non segmented hemivertebra
fused to an adjacent segment
schmorl’s nodes

-herniation of nucleus through end-plate -helmet shaped defect 1/3 of end plate -DDD
nuclear impression/persistent notochord

-shallow indentation posterior 2/3 of inf end plates -cupids bow on AP
Lumbosacral transitional segment (LSTV)
-castellvi grading -only IIa or IIB cause LBP -4-10%
facet asymmetry/ tropism
-acquired due to abnormal biomechanics -if multiple segments then usually patient is rotated or laterally flexed distorting the image
knife clasp
-long L5 SP -SBO of s1 -type 1 has wide SBO at S1 -type 2 has Narrow SBO -type 3 has a sacral ossicle
Srb’s Anomaly

-partial or complete fusion of the 1st and 2nd ribs
Pectus Excavatum

-funnel chest -heart often displaced to left with right heart border over the spine -evaluate for straight back syndrome
Developmental Dysplasia of Hip with Putti’s triad
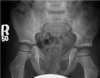
-hypoplastic femoral epiphysis -lateral and superior subluxation of femoral head -shallow acetabulum -often forms accessory articulation -if found early treatable
sacral agenesis aka regression syndrome

-caudal regression syndrome -often associated with gestational diabetes











