Respiratory Viruses II Flashcards
(50 cards)
Parainfluenza Viruses
- Paramyxovirus genus of Paramyxoviridae family
- 4 serotypes
- Significant antigenic drift or shift does not occur
Paramyxovirus Structure
- Single-stranded (-) RNA (one linear piece)
- Nucleoprotein covers RNA
- M (matrix) protein surrounds nucleoprotein complex
- envelope contains attachment protein that has both H and N and the fusion protein (F).
- Pleomorphic

Paramyxovirus Replication
- All events occur in the cytoplasm
- Replicates like (-) RNA virus
- Budding through cytoplasmic membranes
Paramyxovirus Clinical Disease
- Infants and young children get more serious illness but older adults and people with weakened immune system also gets sick
- Parainfluenza 1: Major cause of acute croup (laryngotracheitis) in infants and young children.
- Parainfluenza 2: Croup in children
- Parainfluenza 3: Severe bronchitis and/or pneumonia in infants under 1 year of age
- Parainfluenza 4: Least common of the group, generally associated with mild upper respiratory illness.
Paramyxovirus Diagnosis
•Clinical picture, serology, virus isolation, RT - PCR
Paramyxovirus Treatment
•No specific treatment or prevention, serious cases may require supportive care
Paramyxovirus Vaccine
•Nasal spray vaccine under development
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Pneunovirus genus of Paramyxoviridae family
- 2 serotypes (A and B)
- forms syncytia in tissue culture
RSV Structure
- Same as parainfluenza virus except the envelope glycoproteins are an attachment (G) glycoprotein and a fusion (F) glycoprotein.
- Non segmented (-) ss RNA genome
RSV Replication
•same as Paramyxovirus
RSV Epidemiology
•RSV infection occurs annually from late fall to early spring
RSV Clinical Disease
- Single most important agent of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants under 1 year of age
- Can infects children and adults
RSV Transmission
•Transmission by contact with infective secretions incubation period 2-4 days
RSV Clinical Findings
- Spreads from upper respiratory tract and goes down to bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
- Acute phase of cough, wheezing and respiratory distress lasts 1 to 3 weeks
- hyperexpansion of lungs, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, interstitial infiltrates
- Fatality: 0.5-1.0%

RSV Pathogenesis
- Infection primarily in respiratory epithelium with progression to middle and lower airways
- RSV F protein promotes fusion leading to syncytia formation
- Major factors in pathogenesis:
- Deficit in humoral response to RSV antigens
- Antigen-antibody complex formation within respiratory tract results in complement activation
- Excessive damage from inflammatory cytokines
- TH2 cytokines associated with severe disease
RSV Immunity
•Immunity to reinfection is brief because recovered patients from a primary acute episode are reinfected with the virus
RSV Diagnosis
•immunofluorescence to detect viral antigen in nasal secretions, RT-PCR

RSV Treatment
•supportive, (aerosol ribavirin in selective circumstances)
RSV Prevention
- No vaccine. A monoclonal antibody against F protein (palivizumab) used for prophylaxis in high-risk infants
- Nasal spray vaccine under development
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV)
- Metapneumovirus genus of the Paramyxoviridae family
- Accounts for 10% of the respiratory tract infection in infants and young children
- Second to RSV to cause acute bronchiolitis with comparable severity and symptoms to those of RSV
- Both RSV and hMPV can infect the same child
- Infection with hMPV occurs in slightly older children compared with RSV
- Diagnosis: RT-PCR (amplification of the viral genome)
Coronavirus
- Coronavirus genus of the Coronaviridae family
- alpha (human coronavirus) and beta (SARS Cov-1, MERS CoV SARS-CoV2 (COVID-19), bat, mouse hepatitis, bovine, human)
- Cause respiratory, gastrointestinal, CNS diseases in human & animals
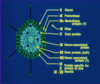
Coronavirus Structure
- Large, enveloped, (+) ssRNA, helical nucleocapsid virus
- 125-150 nm in size
- RNA genome size 27- 32kb
- Envelope spike glycoprotein S1 binds to receptor (ACE2 for SARS), S2 helps in fusion
- Other proteins: HA acetylesterase glycoprotein and Membrane glycoprotein
Coronavirus Replication
i. Replicates in the cytoplasm like (+) RNA viruses
ii. Genomic and sub-genomic RNAs are made
iii. RNA dependent RNA polymerase and other proteins form the complex for transcription and replication
iv. Encodes an enzyme for proof reading of genome ability
v. Buds through endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi
Coronavirus - human coronavirus
•229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1 – 10-30% of common cold; runny nose, sore throat, fever, headache, cough