Restless Earth Flashcards
(45 cards)
Continental Crust (3 points)
- Is the land
- thick and less dense
- 30-50km thick
Oceanic Crust (3 points)
- found under oceans
- thin but dense
- usually 6-8km thick
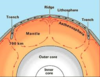
Order of Earth Layers (4 points)
- Crust
- Mantle
- Outer Core
- Inner Core
What is the lithosphere?
the crust and upper most solid mantle
Where is the asthenosphere?
It is part of the mantle
What is the physical state of:
- Lithosphere?
- Asthenosphere?
- Lower Mantle?
- Outer Core?
- solid
- partially molten
- solid
- liquid
Geothermal:
Heat from inside the earth produced by the radioactive decay of elements such as Uranium in the core and mantle.
Convention currents (3 points)
- occurs in mantle
- driven by the heat of the core
- move tectonic plates of Earth’s surface
Magnetosphere:
A huge invisible magnetic field that protects the earth from harmful radiation and is made by he outer core.
Pangea:
when the continents were all joined together. Sometimes known as continental drift.
How many tectonic plates is there?
15
Plate boundary:
Where two plates meet together
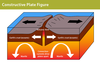
constructive plate boundary (4 points)
- two oceanic plates
- moving away from each other
- earthquakes caused by friction
- shallow sided volcanoes form
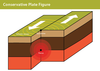
Conservative plate boundary (3 points)
- plates sliding past each other
- friction causes earthquakes
- can move in different or same direction
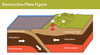
Destructive plate boundary (5 points)
- oceanic plate and continental plate
- moving towards each other
- dense oceanic plate is subducted
- pressure builds causing earthquakes
- very steep destructive volcanoes
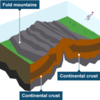
Collision plate boundary (4 points)
- two continental plates
- moving towards each other
- plates buckle and form mountains
- powerful earthquakes formed
Constructive plate boundary example:
Iceland
Destructive plate boundary example:
Monserrat
Conservative plate boundary example:
Loma Prieta
Collision plate boundary example:
Kashmir
What do convection currents look like?
What does a collision plate boudnary look like?
What does a conservative plate boundary look like?
What does a destructive plate boundary look like?