Review of lower limb Flashcards
(123 cards)
Shenton’s line is between which two areas of the hip joint? [2]
Superior pubic ramus - inferomedial border of the neck offemur
L has neck of femur fracture: shenton line not normal

The hip joint’s stability is increased by which three ligaments [3]
Which is the strongest? [1] - Why is this clinically significant? [1]
Pubo-femoral ligament
Ilio-femoral ligament- strongest & found on anterior aspect of the joint - so anterior more strong than posterior
Ischio-femoral ligament
Together - they push the head of the femur into the hip

Which is the ligament found within the hip joint that strengthens the joint? [1]
Ligamentum teres

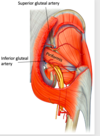
Describe the blood supply to the head and neck of femur [
Profunda femoris: give off medial and lateral circumflex arteries
- from these two arteries get Retinacular arteries- majority of blood to head and neck
Obturator artery: Artery to the head of the femur

The obturator artery is important for which patient population & why? [2]
Paedatric population: important for ossification for head of femur
line things
Which qudrant do you used for IM injection?
A
B
C
D

Which qudrant do you used for IM injection?
A - avoid sciatic nerve
B
C
D
nerve supply in the pelvis
Gluteus maximis inserts onto which structure? [1]
Which nerve supplies gluteus maximus? [1]
Inserts onto iliotibial band
Supplied by inferior gluteal nerve
Which nerve supplies gluteus medius and minimus? [1]
What movement do they cause? [1]
Superior gluteal nerve
Hip abduct and internally rotate the thigh
Tensor fascia lata
Lateral rotators
How do gluteus minimus and medius work to provide hip stablity? [1]
How does gluteus minimus and medius damage present? [1]
Opposite side contract when you walk to stop hip dropping,
Damage to them causes contralateral hip drop / Positive Trendelenburg test

thigh compartments
Sciatic nerve
What are the borders of the femoral triangle? [3]

Superior border: inguinal ligament
Lateral border – medial border of the sartorius muscle.
Medial border medial border of the adductor longus muscle. The rest of this muscle forms part of the floor of the triangle.
Order of neurovascular in femoral triangle? [4]
NAVL:
Nerve
Artery
Vein
Lymphatics

What are the borders of the popliteal fossa? [3]
Medial superior: semimembranosus and semitendinosus
Medial inferior: Gastrocnemius
Medial lateral: bicep femoris
Medial inferior: Gastrocnemius

After leading the popliteal artery
- what is the anteiror segment?
- what is the lateral sgement?
- what is the posterior segment?
Anterior
* anterior tibial: dorsalis pedis
Lateral
* perforating branches of deep penoneal (fibular)
Posterior
* posterior tibial: medial and lateral plantar
Neck of femur fractures (typically with significant displacement) will classically present with a [] and [] rotated limb.
Neck of femur fractures (typically with significant displacement) will classically present with a shortened and externally rotated limb.

NICE recommends offering total hip replacement over hemiarthroplasty in patients whom are [3]
- Able to walk independently outdoors with no more that one stick
- Not cognitively impaired
- Medically fit for the operation
Which muscle is responsible for shortening of the limb and external rotation following a NoF fracture? [1]
Iliopsoas
Common complication of posterior hip dislocation? [1]
Sciatic nerve involvement
Presentation of patellar dislocation? [1]
Knee held in flexion