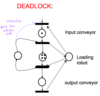
REVISION Control stuff Flashcards
(50 cards)
What are the different aspects of operation automation?
What aspects of an operation to automate?
SENSE: info gathering
ANALYSE with REQUIREMENTS then
DECIDE: generate decision operations and selections which guide operation
ACTUATE: provide automatic or guided manual support
OPERATION

Define automation
Definition of Automation – the part or full replacement of human based functions with a machine, computer or other device
What makes automation hard?
What makes automation hard?
- Complex logic
- Concurrent operations
- Constraints e.g. Limited resources
- Many different operating patterns
- Human interfacing
What are the downsides of automation?
What are the downsides of automation?
- Cost
- Complexity
- Flexibility
- “Experience effect”
- Un-noticed errors
- Job losses
- Trade off in balancing benefits/downsides
What are the reasons for automation?
What are the reasons for automation?
- Labour productivity
- Speed
- Efficiency
- Reliability/repeatability
- Health and Safety
- Infeasible
Backdrop
- Competing against low cost countries
- Increased wage expectation
- Reduced funds available
- Desire for greater profits
- Tasks unsafe
- Impossible to do any other way

What are the two approaches for the effective control of machining operations
Two approaches for the effective control of machining operations
- Better machine design (Bill)
- Design of effective control systems
NOT MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE

What are the different needs for control systems
Need for control systems
- Not all deflections in a machine can be dealt with in design
-
Static deflections
- Unknown & varying workpiece size, shapes
- Different loading positions
-
Dynamic deflections/vibrations
- Dependent on different material/tool combinations can’t allow for all of them
- Different external vibration sources
-
Thermal deflections
- Unknown heat sources
- Difficult to predict heat paths & thermal responses exactly
What are the different types of control and their characteristics
Proportional control
- Quick response
- Disturbance rejection
- Always steady state error
- Might cause stability problems
Proportional integral control
- As above +
- Zero steady-state error
- Might cause stability problems and oscillations
Proportional integral derivative control
- As above +
- Improved stability
- Increased damping
- Sensitive to noise
What are the costs and benefits of closed loop systems?
Benefits of C/L
- Accuracy
- Respond to changes
- Reject disruptions
- Less precision required in actuation
Costs of C/L
- Additional sensors
- More complex control
- More maintenance
- Potentially unstable
What is adaptive control?
Adaptive machine control
- For expensive machines additional control requirements are sometimes employed
- Advanced control for machining is defined as the on-line adjustment of process parameters for the purpose of:
- Optimising production rate (using feed rate)
- Optimising quality (force, speed)
- Minimising cost of materials and components (force, speed)
- Protecting machine (force, torque, power)

What are the two types of adaptive control?
Two types of adaptive control
- Adaptive control constrained (ACC)
- Places a constraint on a process variable
- E.g. if the thrust force and cutting force is excessive, the AC system will change the cutting speed to lower the cutting force
- Adaptive control optimised (ACO)
- Systems that optimise an operation
- E.g. maximising removal rate
- More complex to implement
What are the different sensing issues?
Sensing issues
- Cost
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
- Repeatability
- Reliability
- Maintainability
Need to consider the number, type and location of sensors. The cost of purchase, installing and maintaining sensors has to be balanced by improved performance.
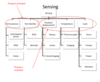
Difference between direct sensing and indirect sensing?
Direct
- Accurate
- Complex to install, maintain and expensive
Indirect
- Simpler to maintain and cheaper
- Less accurate
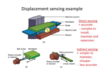
What is the difference between NC and CNC?
Numerical control – method for controlling the movements and support operations of machining components via the insertion of coded instructions (typically numerical) from a computer or other mechanism
Computer numerical control – integrates computer-based instructions into NC machines. Either via remote programming or integration of a computer/microprocessor as an integral part of the machining unit

What does an NC prgramme comprise?
An N.C. programme comprises
- Header (preparatory) – cancels pre-existing settings, sets data types, data units, tool prep, turns on coolant
- Body (main tasks) – moves tool into place, performs tasks, moves tool to safe place
- End (completion) – stop tool, terminate program

What are the two categories of offsets in a machine tool?
Tool and workpiece datum/ reference points considerations
- Offsets are used to redefine the workpiece relative to the datum points in manufacture of machine tool
- Two categories of offset
- Zero offsets define the workpiece datum relative to machine
- Tool offsets which define the tool cutting point relative to the tool reference point
What are the different categories of tool offset compensations?
- Tool length compensation – allows programmer to program all tools as if they are of equal length
- Tool nose radius compensation – used in turning machines
Cutter radius compensation – causes the controller to alter the programmed path to allow for differences between actual and programmed cutter
What is a manufacturing robot?
What is a manufacturing robot:
A re-programmable device designed to both manipulate and transport parts, tools or specialised manufacturing implements through variable programmed motions for the performance of specific manufacturing tasks

What are the different robot types and DOFs
Robot types and DOFs
Anthropomorphic: 6 DOFs
Delta: 6 DOFs
SCARA: 4 DOFs
Cartesian: 3 DOFs

What are the different robot performance measures?
Robot performance measures
- Operation selection
- Working volume
- Payload
- Speed
- Operation performance
- Resolution
- Accuracy
- Repeatability
- Safety
Compare the different robot types
Cartesian: Big reach, low speed, high-ish payload, high repeatability
Anthropomorphic: High reach, average speed, high payload, low repeatability
Scara: high speed, average reach, high repeatability, low payload
Delta: high speed, low reach, low repeatability, low payload

What are the three basic methods for programming robots?
- Teach mode
- Lead through
- Off-line
What are the pros and cons of the different programming methods?
Teach mode
Pros
- Simple widely used technique
- No additional infrastructure required during programming
Cons
- Time consuming and repetitive
- Limited automated testing and verification
Lead through
Pros
- Mimics complex trajectories used by skilled operators
Cons
- Difficult to deal with large robots
- Inaccuracy’s in programming can’t be edited
Off-line
Pros
- Reduced down time during in programming
- Assists cell design and allows process optimisation
Cons
- Requirement for accurate CAD models of instillation
- Accuracy of robot is critical when suing off-line programming techniques