Risk and Insurance Flashcards
(22 cards)
What is certainty equivalence and how do you find it?
- there is a sure amount yc which gives the same utility as the expected utility of the prospect
- yc ~ ŷ0 = π1(y1) + (1-π1)y2
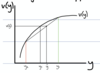
Show the risk premiums and explain their significance.
- rmin = Minimum premium firm would allow, means they break even.
- rmax = Most a customer would pay for insurnace, what ever happens, would be left with v(ŷ)

Why is the second derivative of the utility function not a suitable method of quanifying risk aversion?
- Using an affine transformation of utility functions, we must have the same preferences still
- v(y) into g(y) = a +bv(y)
- but g’‘(y) = bv’‘(y)
- bv’‘(y) is not v’‘(y) so cannot use
What is a fair bet?
A fair bet has the following properties:
- certain income ŷ
- pays Zs with a probability of πs
- Expected value of 0
How do you prove the Arrow-Pratt Measure of risk aversion?
- Approximate v(ŷ + Zs) using taylor series
- Multiply this by πs and sum over s
- Approximate v(ŷ - r) using taylor series expansion
- Equate and rearrange

What is the formula for absolute risk aversion?
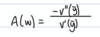
What is the formula for relative risk aversion?
R = (A(y))y
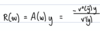
How does an insurance firm work out what level of q corresponds to full cover?
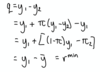
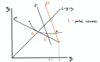
Draw the State contingent income diagram and explain the points on the diagram.
- C = full cover
- E0 = expected income locus, movements along line show insurance levels
- I0 = agent indifference curve for prospect
- yc = certainty equivalence
- ŷ = full and fair insurance

Write down the income states for a full and fair insurance contract øFF = (pF, qF).
Good state: y = y1 - p
Bad state: y = y2 - p + q
ŷø = π(y2 - p + q) + (1-π) (y1 - p)
=π(y1 - L - p + q) + (1-π) (y1 - p)
= y1 - p
What are the assumptions for competitive insurance?
- Zero Profit condition - firms break even
- Free entry condition - if a better break even contract is available, another firm can come and offer it
- High and low risk types - firm cannot distinguish but knows the proportion (lambda)
Show how a seperating equilibrium works in a symmetric info model.
- Good and bad types are known
- Seperate contraacts offered Øi = (pi, qi)
- Market is competitive for fair premium is charged
- Full and fair insurance is taken
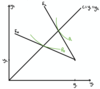
What is adverse selection in the insurance market?
HIgh risk types save money if they pretend to be low risk
Full and fair insurance cannot be offered as firm would go bust
What is a pooling equilibrium?
Contract offered using average probability to calculate premium.
HOwever, new firm can enter and offer a contract at X
This is preffered but low risk but not high risk so all the low risk choose it
The original firm goes bust as it is left with just high risk.
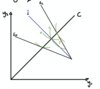
Explain how a seperating equilirbium works in an asymmetric info model.
- Contracts A and B are offered
- High risk take A as A~B but A is full (risk averse)
- Low risk takes B as B>A, its only partial insurance but its better than nothing
- Both break even
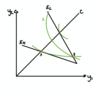
What is the potential issue with the seperating equilibrium?

Why do high and low risk individuals have different indifference curves?
due to different probabilities, NOT diff attitudes to risk
What is moral hazard in the insurance market?
- A market failure which arises from inability to observe behaviour ex-post
- Probability of loss now endogenous
- 1 type of person, π depends on cost of care (a)
- a=0 no cost of care, a=1 cost taken
*
How does the moral hazard affect an insurance market full symmetric info?
No issues
different premiums depending on a

HOw does moral hazard affect the insurance market when there are hidden actions?
If a canno tbe observed, firms can be fooled into thinking customer has taken cost of care.

How does an insurance firm change to combat moral hazard?
Incentive compatibility
Choice of care to be consistent with contract
Partial cover for a=1
a=0, indiff between E1 and E2 but choose full insurance
There is no longer an incentive to cheat.