Runway slope, Considerations, The TO (16/21-05-18) Flashcards
(51 cards)
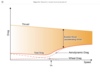
What happens to ASD, and therefore TOR, TOD & LD, with a runway up slope?
ASD will increase
TOR & TOD will increase
LD will reduce
What happens to ASD, and therefore TOR, TOD & LD, with a runway down slope?
ASD will reduce
TOR & TOD will reduce
LD will increase
How much will ASD increase for every 1% of slope?
it will increase by 5%.
How much will ASD decrease for every 1% down slope?
We aren’t interested due to it being safer than already required.
What is TODR and what is it’s relationship to TODA?
Take Off Distance Required, a minimum legal length of runway needed to take off, including a safety factor.
TODR must be <= TORA
What considerations must be apply to wind on TO?
With a head wind we are only allowed to include a max of 50% of total wind in calculations.
With a tail wind we must account for 150% of the tailwind in calculations.
When are we allowed to include reverse thrust in stopping calculations?
When the runway is wet.
What is Field length limited TOM (FLLTOM) / Runwau limited TOM (RLTOM)?
The TOM that we are limited to due to being able to reach the required speed from the TODA.
What are the threats associated with airframe icing?
Increased mass
increased drag
change in handling
What are the threats associated with super cold fuel?
Can affect fuel delivery
What are the threats associated with runway contamination?
TOR increases (spray impingement drag, wheel drag, thrust loss)
TOD increase (same)
ASD increase (reduced friction)
LD increase (same)
Directional control is reduced
What is considered a contaminated runway?
when more than 25% of the runway is covered by more than 3mm of water of equivellent in slush, snow or ice (they will be less)
a wet runway in not considered contaminated.
In winter contamination conditions with a compacted snow/specially prepared winter runway, how is TOR, TOD, ASD and LD affected?
TOR & TOD will be unaffected
ASD & LD will increase
What affect will a wet runway have on TOR, TOD, ASD and LD?
TOR & TOD will be unaffected
ASD & LD will be increased
What are Aircraft Classification Numbers/Pavement Classification Numbers?
A code that can be used to determine if an aircraft is able to use a certain runway due to structural considerations.
How will you know if an aircraft of mass <= 5700kg will be able to use a runway?
Max mass and max tyre pressure will be written on an appropriate Aerodrome plate
How will you know if an aircraft of mass > 5700kg is able to use a runway?
By checking if it’s ACN is <= the runways PCN.
How are PCNs reported?
4 letter code
first letter is pavement type
R - rigid (concrete slab)
F - flexible (series of layers)
In overload operations, when can ACN exceed PCN by 10%?
Occasional movements
when the runway is older than 12 months
When only 5% of movements exceed PCN annually
There are no signs of damage
In overload operations, when can ACN exceed PCN by 25%?
In addition to 10% requirements:
the runway is regularly inspected.
In overload operations, when can ACN exceed PCN by 50%?
In addition to 25% requirements:
There is an inspection before and after each overload movement
In overload operations, when can ACN exceed PCN by more than 50%?
In emergencies
What is the brake release point?
The place on the runway where you must hold the aircraft in place until TO thrust is achieved.
What happens to your TO data if you don’t use the BRP?
Your TO data will be invalid.