Science Team Content Testing Flashcards
Test Deck (177 cards)
Testing . . .

4 . . 5. . . 6
Please define the following term:
Henry’s Law
At a constant temperature, the amount of a given gas dissolved in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid.
Pgas=kHc
P= partial pressure of the solute in the gas
kH= constant with dimensions of pressure divided by concentration.
c= concentration of the solute
Which gases diffuse in and out of blood during respiration?
- Oxygen diffuses into the blood
- Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood
Please identify and explain the following process depicted by the image:
The process depicted is inhalation. When one inhales:
- The diaphragm contracts and moves downward
- The rib cage expands outward
- The lungs expand due to the resulting increase in volume and decrease in pressure of the chest cavity
- Air is drawn in as the decrease in pressure falls below the atmospheric pressure
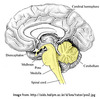
The three brain structures that regulate respiration are: 1. Midbrain, 2. Medulla Oblongata, 3. Pons
All three make up the brainstem.
Define Macrophage
A macrophage is type of white blood cell. Macrophages (Greek for “big eaters”) phagoctyose (engulf and digest) cellular debris and pathogens. They are found throughout the human body as either mobile cells that act throughout the lymphatic system or as stationary/fixed cells that act in high risk areas for microbial infection such as the alveolus of lungs, the liver, the spleen, bone, and connective tissue.
Define differential pressure.
The difference between pressure inside the lung, called intrapulmonary pressure, and pressure outside the lung, called intrapleural pressure.
How is surface tension created in the lungs?
The walls of the aveoli are coated with a thin layer of water, and the strong attraction between water molecules creates surface tension
What potential problems could this surface tension lead to?
When exhalation occurs, the area between aveoli decreases, and therefore increases the strength of the surface tension. This could prevent another expansion of the aveoli (and lungs) and prevent further breathing.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA is a polymer of ________, which are held together by ________ bonds.
nucleotides; phosphodiester
Label the 5’ end and the 3’ end of this single DNA strand.

The 3’ end carbon is attached to an -OH group and the 5’ end carbon is attached to a phosphate group.

Describe what is meant by the antiparallel nature of DNA.
The two strands of DNA that make up the double helix run in opposite directions, one strand with a 5’ -> 3’ orientation and the other with a 3’ -> 5’ orientation.
What are the three main parts of a nucleotide?
a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base
Name the purines and pyrimidines.
The purines are adenine and guanine. The pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine.
What is the difference in structure between purines and pyrimidines?
Purines are two ring structures while pyrimidines are single ring structures.
Which nitrogenous base forms hydrogen bonds with adenine?
thymine
Which nitrogenous base forms hydrogen bonds with guanine?
cytosine
Which type of bond forms between the nitrogenous bases of two complementary DNA strands?
hydrogen bond
How many hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine?
two hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds form between guanine and cytosine?
three hydrogen bonds
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA is transcribed to RNA which is translated to amino acids that make up a protein.
Define DNA helicase.
an enzyme responsible for separating the two strands of a DNA double helix needed for initiation of DNA replication





