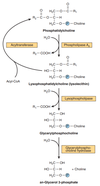
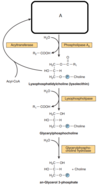
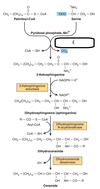
Semi-final pool the rest (organized) Flashcards
(768 cards)
Which amino acid is an activator of N-acetyl-glutamate synthase?
Select one:
a. glutamine
b. lysine
c. arginine
d. aspartate
e. asparagine
The correct answer is:
c. arginine
In what form is ammonia transported from muscle to the liver?
Select one:
a. asparagine
b. arginine
c. leucine
d. glutamine
e. valine
The correct answer is:
b. glutamine
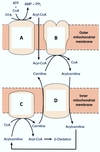
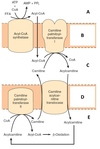
Which hepatocytes express the highest activity of the ornithine cycle enzymes?
Select one:
a. periportal
b. pericentral
c. perivenous
d. centrolobular
The correct answer is:
a. periportal
Which amino acid contributes to the increase in the activity of sirtuins?
Select one:
a. tryptophan
b. phenylalanine
c. tyrosine
d. valine
e. glutamine
The correct answer is:
a. tryptophan
What is the effect of acidosis on the activity of glutamine synthesis in the liver?
Select one:
a. increase in the periportal hepatocytes
b. increase in the pericentral hepatocytes
c. decrease in the perivenous hepatocytes
d. decrease in all regions of the lobules
answer:
b. increase in the pericentral hepatocytes
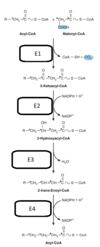
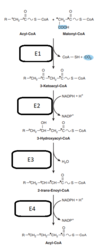
Which amino acid does NOT contribute to the formation of pyruvate in the course of its degradation?
Select one:
a. Alanine
b. Glutamine
c. Tyrosine
d. Leucine
e. spartateAAspartate
The correct answer is:
d. Leucine
Which amino acid can NOT provide any C-atom for the synthesis of glucose in humans?
Select one:
a. Glutamate
b. Isoleucine
c. Leucine
d. Phenylalanine
e. Tryptophan
The correct answer is:
c. Leucine
Which pair of amino acids are released at the highest concentration from skeletal muscle in the fasting state?
Select one:
a. Glutamate, aspartate
b. Glutamine, asparagine
c. Alanine, glutamine
d. Alanine, leucine
e. Valine, leucine
The correct answer is:
c. Alanine, glutamine
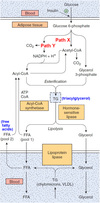
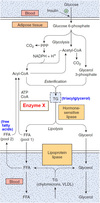
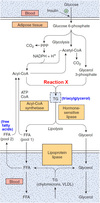
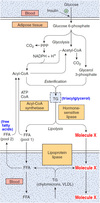
What happens in the course of glutaminolysis?
Select one:
a. Glutamine is converted to aspartate
b. Glutamine is converted to asparagine
c. Glutamine is completely oxidized to CO2 and water
d. Glutamine is converted to glucose
The correct answer is:
a. Glutamine is converted to aspartate
Which amino acid is the most common source of the 1C-groups transferred by tetrahydrofolate?
Select one:
a. Alanine
b. Serine
c. Threonine
d. Isoleucine
e. Methionine
The correct answer is:
b. Serine
Deficiency of which vitamin would cause enhanced excretion of methylmalonate in the urine?
Select one:
a. B1
b. B2
c. biotin
d. B12
e. D
The correct answer is:
d. B12
Which amino acids should be enriched in the diet of a patient with phenylketonuria?
Select one:
a. Phe, Gln
b. Arg, Lys
c. Trp, Tyr
d. Asp, Glu
e. Ala, Glu
The correct answer is:
c. Trp, Tyr
Which interconversion includes glutamic semialdehyde as an intermediate?
Select one:
a. Arginine to Proline
b. Glutamate to Glutamine
c. Glutamate to α-ketoglutarate
d. Methionine to Threonine
The correct answer is:
a. Arginine to Proline
Which vitamin is a co-factor in the synthesis of hydroxyproline?
Select one:
a. B1
b. B2
c. B6
d. B12
e. C
The correct answer is:
e. C
What is the role of Se in the function of the thyroid gland?
Select one:
a. Se participates in the structure of thyroxine
b. Se participates in the structure of thyroglobulin
c. Se participate in the structure of deiodinase
d. Se forms a complex with iodine to activate it for thyroxine synthesis
The correct answer is:
c. Se participate in the structure of deiodinase
How is the nitrogen balance changed, if the food is depleted of Leu, but all other amino acids are doubled?
Select one:
a. no change
b. negative N-balance
c. positive N-balance
d. positive N-balance only in children
e. positive N-balance only in adults
The correct answer is:
b. negative N-balance
How is the nitrogen balance changed, if the food is depleted of Glu, but all other amino acids are doubled?
Select one:
a. no change
b. negative N-balance
c. positive N-balance
d. negative only in children
e. positive N-balance only in adults
The correct answer is:
a. no change
Dietary supplementation with which amino acid could counteract the sleep-promoting effect of serotonin?
Select one:
a. Glu
b. Trp
c. Leu
d. Lys
e. Arg
The correct answer is:
c. Leu
Which one is a metalloprotease?
Select one:
a. pepsin
b. trypsin
c. elastase
d. carboxypeptidase
e. chymotrypsin
The correct answer is:
d. carboxypeptidase
Which zymogen does not need another protease for its activation?
Select one:
a. trypsinogen
b. pepsinogen
c. chymotrypsinogen
d. proelastase
The correct answer is:
b. pepsinogen
Which amino acid is present in the active site of the proteasome proteases?
Select one:
a. Aspartate
b. Tyrosine
c. Lysine
d. Threonine
e. Trpyptophan
The correct answer is:
d. Threonine
Which metal ion is present in the active site of the matrix metalloproteases?
Select one:
a. Zn2+
b. Fe2+
c. Fe3+
d. Cu2+
e. Ca2+
The correct answer is:
a. Zn2+
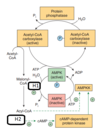
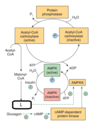
Which amino acid acts as a signal to suppress autophagy?
Select one:
a. Glycine
b. Leucine
c. Glutamate
d. Glutamine
e. Arginine
The correct answer is:
b. Leucine
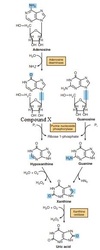
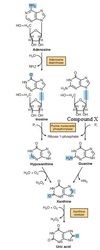
Which compound is the first N-free intermediate released in the indirect deamination of aspartate?
Select one:
a. pyruvate
b. oxaloacetate
c. fumarate
d. α-ketoglutarate
e. methylmalonate
The correct answer is:
c. fumarate