Shoulder/Humerus Flashcards
(56 cards)
What are the findings & dx of this case?

- Non-uniform loss of inferior GH joint
- Inferior Osteophytes at inferior GH
- Concretion type of calcifications in axillary pouch
- OA (or DJD) of GH joint with secondary synovial osteochondrometaplasia
Degenerative joint disease is more common in what area of the shoulder
AC joint (more than GH - GH is likely secondary to something else)
Decrease joint space, subchondral sclerosis, osteophytes, small subchondral cysts are seen in what shoulder condition
DJD/OA
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Supraspinatus tear (R)
(Left is normal)
What are the findings & likely dx of this case?

- Articular surace of humeral head appears absent/resorbed → GH joint not visibile as a result
- DX: Neuropathic Arthropathy (atrophic pattern); septic arthritis, avascular necrosis are less likely ddx
- Reccs: cervical spine MRI for possible syrinx to confirm neuropathic arthropathy
Characteristics of ____ in the shoulder include:
- Sharp amputation of articular ends
- Tapered appearance - “licked candy stick”
- Lack of hypertrophic features
Atrophic Neuropathic Arthropathy
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Atrophic pattern of Neuropathic Arthropathy
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

(syrinx in spinal cord)

Characteristics of ____ in the shoulder include:
- Bilateral symmetric GH & AC joint involvement → typically results in a uniform loss of joint space
- Erosions on the humeral head/greater tubercle
- Erosions at AC joint
- Rotator cuff rupture → resulting in superior migration of the humeral head

RA
What two different conditions are demonstrated here?
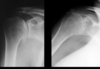

Characteristics of ____ in the shoulder include:
- Erosive changes at superolateralportion of humerus
- Can see enthesopathy at coracoclavicular ligaments
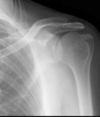
Ankylosing spondylitis
____ is MC location for hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD)
Supraspinatus tendon
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

Hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD)
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


Calcificaiton/OA of both GH joints is suscpicious for ____
Calcium Pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPDD) arthropathy
Characteristics of ___ include:
- Unusual distribution, GH joint
- Unusual intraarticular distribution
- Prominent subchondral cysts
- Severe, subchonral bone changes
- Variable osteophyte formation
CPDD
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?


What condition is likely the cause of these findings?

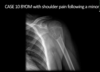
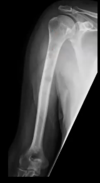
Acute transverse fx through mid clavicle
- Mechanism of injury usually fall on an outstretched hand or direct trauma
- Medial fragment elevated by the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- MC type
What type of clavicular fx?
Middle
- Mechanism of injury usually inferiorly oriented forces on humerus and scapula
- Look for intra-articular extension
- 2nd MC (15%)
What type of clavicular fx?
Lateral
What condition is likely the cause of these findings?