Test 3 Vocabulary Flashcards
(127 cards)
Purpose of the Nitrogen cycle?
Convert N to a usable form
This step of the N cycle converts N2 —> Ammonia and nitrates
Fixation
During this step of the N cycle, bacteria and fungi break proteins in dead plant/animal material down to amino acids
Mineralization/Ammonification
During this step of the N cycle, ammonia is oxidized to nitrate and nitrite
Nitrification
During this step of the N cycle, nitrates are reduced to N2 by organisms for oxygen
Dentrification
Name the correct order of steps for the nitrogen cycle
Fixation —> Mineralization/Ammonification —> Nitrification —> Dentrification
In the Phosphorus cycle, what does POP stand for?
Particulate Organic Phosphorus
In the Phosphorus cycle, what does DIP stand for?
Dissolved Organic Phosphorus
In the Phosphorus cycle, what does DOP stand for?
Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus
Relative allocation of resources to survival and reproduction, and details of timing
Life History
Distribution vs. Dispersion
Pattern of individuals on the landscape
Statistical model that predicts random dispersion
Poisson Distribution
Highly determinate; individual and unbranched, motile; reproduce sexually
Unitary Organism
Indeterminate; branched; sessile; reproduce vegetatively/asexually [hard to determine the individual]
Modular Organism
Genet
A genetic individual [such as grass]
Example of a Ramet
Individual stem/trunk
Reproduces only once per lifetime [annuals, biennials, indeterminate, continuous]
Semelparity
Reproduce 2+ per lifetime [overlapping, continuous]
Iteroparity
What is cultural eutriphication? Give a fresh and salt water example.
When man speeds up the process of enrichment and eventually causes the area to become a dead zone Salt - the Gulf of Mexico has a dead zone as a result of agriculture near the Mississippi; as it rains, everything in the fields washes off and travels to the ocean Fresh - adding phosphate rich fertilizer to a river causes an algal boom (using all the CO2); when the algae die, microorganisms decompose the dead algae and deplete all oxygen in the river, causing a dead zone
What is the N:P ratio in a saltwater environment? In fresh water?
1:8, 1:23
In reference to Tilman, define a ZGI and what it stands for.
Zero Growth Incline - the minimum amount of a resource the organism needs to survive
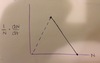
Which Tilman graph is this? State its significance.

Essential. The species gets an essential amount of nutrients but will need more of the other nutrient for a more balanced diet.
Which Tilman graph is this? State its significance.

Antagonistic. It would be better for the organism to eat either one resource or another because it would be detrimental to eat both.
Which Tilman graph is this? State its significance.

Perfectly Substitutable. Either resource is fine and can be substituted in equal amounts.