The Medicine Semester 1 Flashcards
(78 cards)
What is the formula for molarity?

What is the formula for molality?

What is the formula for equivalents?
Eq= ionic valency x number of ions in solution
What shape and bond angle does an sp3 hybridised molecule have?
Tetrahedral shape with a 109 degree bond angle
What shape and bond angle does an sp2 hybridised molecule have?
Planar (trigonal) shape with a 120 degree bond angle
What shape and bond angle does an sp hybridised molecule have?
Linear shape with 180 degree bond angle
Which is more stable and why?

Staggered conformation is more stable
Less energy and reduced rotation as H atoms are as far away from eachother as possible
What is the dihedral/torsion angle?
The angle formed between two intersecting planes
In chair conformation which is preferred? Axial or equatorial?
Equatorial as it provides less steric strain
What causes E/Z isomerism and how are the isomers distinguished?
Lack of rotation around a double bond causes E/Z isomerism
If the two groups with the highest priority (largest molecular weight) are on the same side of the double bond, the Z isomer has formed.
If they are on opposite sides, it is the E isomer.
In optical isomerism how are the R/S isomers distinguished?
Group with the lowest priority (usually H should be drawn facing backwards
The three other groups should be numbered in order of priority, if the numbers read in a clockwise direction (1,2,3) it is the right handed (R) isomer
If they read in an anticlockwise direction, it is the left handed (S) isomer
What quantities are given for the differing solubilities?
(Think parts of solvent:1 part of solute)

Define solubility
The maximum amount of solid that can be dissolved
Define dissolution
The transfer of molecules from solid to liquid state
What is the common pharmaceutical name for the solvent within a drug?
The vehicle
What causes solubility to decrease?
Increased molecule size
With smaller surface area
With presence of hydrophobic regions
Presence and position of substituents
What other factors affect solubility?
Solid state (crystalline/amorphous)
Polymorph type
Salts and counter ions
Composition of aqueous media (buffer)
Ionic strength
Temperature
Define miscibility
Mutual solubilities within a liquid-liquid system
What is the dielectric constant?
It measures the ability of a substance to be able to store electrical energy within an electric field
What is the equation for Ka?

What is the equation for pH?

What is the equation for pKa?
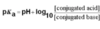
What are the equations for % ionisation of weak acids and weak bases?

What is the relationship between pH and pKa at 99%, 50% and 1% ionised?




