Theory Midterm Flashcards
(148 cards)
What is parasitism?
One organism benefits while the host is harmed
List the steps of blood flow through the heart
- Superior and inferior vena cava
- Right atrium
- Tricuspid valve
- Right ventricle
- Pulmonary valve
- Pulmonary artery
- Lungs
- Pulmonary veins
- Left atrium
- Mitral valve
- Left ventricle
- Aortic valve
- Aorta
What is an example of an opportunistic pathogen?
E. Coli entering the abdominal cavity
How does the autoclave kill microbes?
By coagulating proteins
What is commensalism
One organism uses another to meet its needs but causes no harm to the host
What is aseptic technique
practices and procedures used to avoid introducing pathogens into the wound
What does N. gonorrhoeae cause?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (gonorrhoeae)
What is secondary intention?
Happens when primary intention fails Common in large wounds or postop SSI’s where infection has damaged the tissue The wound is not sutured and left open to heal from the inside out
Pressure, temp, use, and time for gravity air displacement
- 15 to 17 psi
- 250F
- Used for wrapped items
- 15 to 30 minutes
What is an opportunistic pathogen?
Microbes that are harmless under normal circumstances but may become harmful in a weakened host.
What happens when endotoxins enter the blood stream?
Septicemia
What is shelf life?
The length of time a package in storage remains sterile
How are bacteria classified?
By shape
What are obligate anaerobes
Require the level of oxygen found in a typical room
Poisoned by oxygen
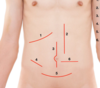
In which quadrant is the liver located
Right upper quadrant
When is intermediate disinfection used?
Large areas such as floors
Used for terminal cleaning
What degree of wound healing is this?

Primary (union, first intention)
Pressure, temp, use, and time for flash sterilizer
- 27 psi
- 270F
- Used for unwrapped items in emergency situations
- 3 minutes for unwrapped items without a lumen
4 minutes for instruments with lumens or marking tape (prevacuum)
10 for gravity displacement
What does C. difficile cause?
antibiotic associated GI disease
Extreme shits
What are cells stained with?
Crystal violet with safranin
How should dirty instruments be transported to decontam?
They should be covered
In which quadrant is the spleen located
LUQ
Chemical used for intermediate disinfection?
Phenol (carbolic acid)
Transmission and effects of Hep C
Blood-borne RNA
Blood and blood products
Effects the liver