Unit 4 Flashcards
(79 cards)
At phase __- of cardiac AP what rushes inwards?
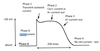
Na current, depolarizing cell
what happens at Repolarization of Cardiac AP?

Na channels close,
brief activation of Ito -> transient outward current
what happens at the plateau stage of repolarization in Cardiac AP?

Ca cells rush in, K rush out
What happens in phase 3 of cardiac AP, the later stage of repolarization?

just K goes out
With Cardiac AP, what is the rise represented by the blue line?

Calcium influx
How do you know that the red line is the cardiac curve?

Because the tension is increasing between B and C, where myofilament are overlapped
What does contractility INC with NE admin?
ne binds to b1 adrenergic receptors -> causing

ne binds to b1 adrenergic receptors -> INC in Ca rlease from SR
Ne INC AP ___ and ____ before it causes an INC in tension

amplitidue and duration
In this graph of twith duration, which is control and which is afrer norepi admin?
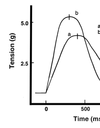
B is after norepi
ionotropic INC the rise in tension, but shortens the contraction duration
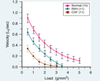
This line represents an increase in ____ to ____
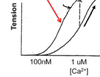
INC in sensitivtiy to calcium (due to drugs or inc sarcomere length)
the ____ line is with Norepinephrine admin

top, INC in Ca -> INC in contractility -> INC upwards
which yellow line is INCREASED compliance in this End diastolic pressure curve?

lower line
the red line represents a ____ in ionotropy with End Systolic VOLUME relationship

decrease
what does the shift to the left represent?

hemorrhagic shock
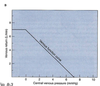
for venous system, compliance is HIGH when transmural pressure is ___.

low
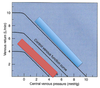
which line represents an older person (compliance decreases with age)

right..
slope is 1/compliance
shift to the right due to ____ attack
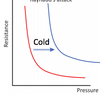
Raynaulds
with fibrosis lung compliance is DECREASED so its curve is ___ than normal

lower
with emphyesma lung compliance is INCREASE so its curve is ___ than normal
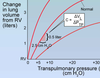
higher
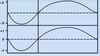
____ and ____ are both zero at the begninng and end of inspiration
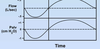
during ___ all curves have higher PEAKS

vigorous exercise
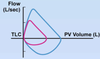
During ____, no plateau is reached in the IVPF curves

inspiration
maximal flow rate increases with ____ lung volumes.

increasing
resistance INC for the first ___ generations than falls as cross secitonal area increase
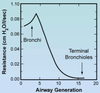
three