VETS3010 Viral families Flashcards
(62 cards)
Briefly describe Adenoviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- dsDNA virus w intranuclear replication and inclusion bodies
- Icosahedral capsule w 1-2 fibers/vertex
- non-enveloped
- many serotypes, most species specific; can persist for years

List some examples of Adenoviruses
- Infectious canine hepatitis (Canine adenovirus 1)
- Infectious canine laryngeotracheitis (Canine adenovirus 2)
- human adenoviruses (>30 serotypes)
- bovine adenoviruses (10 serotypes)
- porcine adenoviruses
- equine adenoviruses
- avian adenoviruses
List some examples of Circoviruses
- Psittacine beak and feather disease virus
- Chicken anaemia virus
- Porcine circovirus
- Canine (dog) circovirus
Briefly describe Herpesviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- dsDNA w intranuclear replication
- Icosohedral capsid
- Enveloped
- Characteristic feature: latent infection with periodic recurrences

List some examples of herpesviruses
Avian:
Infectious laryngotracheitis
Marek’s disease
Bovine herpesvirus 1-5:
Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (BHV1)
Bovine herpes mammilitis (BHV2)
Bovine malignant catarrhal fever (alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 + ovine herpesvirus 2)
Canine herpesvirus 1
Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 1-8
Equine herpesvirus 1-7
1: Equine abortion virus
2, 5: Equine cytolomegaloviruses
3: Equine coital exanthema
4: Equine rhinopneumonitis virus
Feline herpesvirus 1 (Feline rhinotracheitis virus)
Human herpesviruses:
Herpes simplex 1-8
Varicella zoster
Epstine Barr virus
Porcine herpesvirus 1 (Aujeszky’s disease)
How are herpesviruses usually diagnosed?
Detection of antibodies NB detection of virus only useful during periods of disease recrudence
Briefly describe papillomaviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- dsDNA with intranuclear replication
- Icosohedral capsid
- no envelope
- Characteristic: lesions usually spontaneously regress
- Some associated with carcinomas

How are papillomaviruses usually diagnosed?
Characteristic pathology
EM (mature viruses in keratinised epithelium)
PCR (genomes present in basal cells)
(No success with culture)
List some examples of papillomaviruses
Human papilloma viruses (>60 types)
Bovine papillomaviruses 1-6
Equine papillomaviruses Equine sarcoids (bovine papillomavirus)
Canine papillomaviruses
Ovine papillomas
Caprine papillomas
Briefly describe parvoviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features
- ssDNA with intranuclear replication + inclusion bodies
- icosohedral capsid (very small virus)
- non-enveloped
- extremely resistant, incluing extreme temp and pH
- highly immunogenic

List some examples of parvoviruses
- Canine parvovirus
- Swine parvovirus
- Feline panleucopenia virus
Briefly describe poxviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- dsDNA, but with cytoplasmic replication + inclusion bodies
- complex capsid, large
- enveloped, but infectious even without envelope (resistant in environment)

How are poxviruses usually diagnosed?
- characteristic clinical appearance and histopathology
- virus isolation & EM
- PCR used less commonly
List some examples of poxviruses
- Smallpox
- Vaccinia
- Buffalopox
- Cowpox
- Sheepox
- Goatpox
- Lumpy skin disease
- Scabby mouth (parapox)
- Pseudocowpox/papular stomatitis (parapox)
- Swinepox (pigpox)
- Myxoma
- Fowlpox
Briefly describe African Swine Fever Virus
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- dsDNA virus
- icosohedral
- enveloped
- taxonomic ‘orphan’
- only DNA arbovirus
Briefly describe Calciviruses
- genome and site of replication?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- ssRNA
- icosohedral capsid with characteristic “cup-shaped depressions” = calices
- non-enveloped
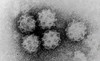
List some examples of Calciviruses
- vesicular exanthema
- feline calcivirus
- rabbit haemorrhagic disease
Briefly describe coronaviruses
- genome?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- ssRNA virus
- helical capsid with “club-shaped” peplomers
- enveloped

List some examples of coronoviruses
- Infectious bronchitis (in chickens)
- Transmissible gastroenteritis (in pigs)
- Porcine epidemic diarrhoea
- Porcine haemagglutinating encephalitis
- Feline infectious peritonitis
- Canine coronavirus
- Bovine coronavirus
- Severe acute respiratory disease (SARS)
- Middle East respiratory distress syndrome (MERS-CoV)
- COVID-19
Briefly describe Flaviviruses
- genome?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- ssRNA virus
- Icosohedral capsid
- enveloped
- mostly arboviruses (biological transmission) (except some pestiviruses)
List some Flaviviruses (Flavivirus genus)
- Japanese B encephalitis
- Murray Valley encephalitis
- Dengue
- West Nile virus
- West Nile virus - Kunjin virus
List some Flaviviruses (Pestivirus genus)
- Bovine virus diarrhoea virus
- Border disease virus
- Swine fever (hog cholera)
Briefly describe Influenza viruses (orthomyoviridae)
- genome?
- capsid?
- enveloped?
- specific features?
- 8x ssRNA
- Helical capsids with H & N peplomers
- enveloped
- Subject to antigenic drift, as well as antigenic shift

List some influenza viruses
- Influenza A, B, C (only A of veterinary importance)
- Subtypes: H1-17, N1-10
- Spanish flu H1N1
- Swine flue H1N1(pdm09)
- Avian influenza H5N1, H7N9, H7N7, H9N2
- Equine influenza H7N7(equi 1), H3N8(equi 2)
- Canine influenza (Dog flu) H3N8
- Fowl plague: H5, H7 subtypes
- All subtypes found in ducks







