Week 2 Flashcards
(221 cards)
Where do mature B-cells reside?
Secondary lymphoid organs
What is B-cell activation?
- A naiive B-cell has not yet recognized its antigen
- When a naive B-cell binds to its antigen, it becomes activated
What is cross-linking?
- When multiple BCR’s on a single B-cell, all with the same specificity, bind to the antigen

How is activation signals conveyed to naive B-cell when it binds its antigen?
- Ig-alpha
- Ig-beta
- Non-covalently associated with BCR and they are responsible for signaling cascade within B-cell

What is the result of B-cell activation?
- B-cell turns into a plasma cell that secretes antibodies
- Antibodies have the exact same specificity as the BCR receptor. The only difference between antibodies and BCR is they are secreted instead of tethered to the membrane.
Structure of antibodies
- 2 light chains
- 2 heavy chains
- Variable regions and constant regions
- Each antibody has 2 antigen-binding sites (variable regions)
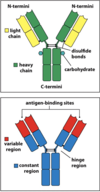
antigen binding site of BCR/antibodies
- There are 2 antigen binding sites
- Each site is made up of 1 variable region of a light chain and 1 variable region of a heavy chain
hypervariable loops of BCR/antibody
- There are 3 hypervariable loops within each V region
- So there are 6 hypervariable loops per antigen-binding site
- These are also called “Complementarity determining regions”
- This is the specific region within the V region that binds the antigen
What do the hypervariable loops recognize?
- Epitope - the specific region of an antigen that the hypervariable region binds to
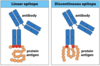
linear epitope
- a linear sequence of amino acids recognized by an antibody

discontinuous epitope
- a sequence of amino acids within the antigen’s folded shape.
- recognized by a BCR/antibody
multivalent antigen
- When an epitope is present multiple times on a single antigen, we call it a multivalent antigen
- BCR stimulation is stronger with a multivalent antigen
*
Can multiple antibodies bind to the same antigen?
- Yes
- BCR A binds to epitope A and BCR B binds to epitope B on the same antigen.
polyclonal response
- When multiple different types of B-cells are activated in resopnse to a single antigen
- Antibodies with the same V-region and antigen specificity can bind to an antigen. But these antibodies can have different C-regions, which dictates the host’s response to the antigen.
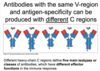
What dictates the immune response to an antibody binding the antigen?
- The C-region of the bound antibody
- The “class” of antibody bound
What are the 5 isotypes/classes of antibodies?
- IgG
- IgA
- IgM
- IgD
- IgE
What is the structure of IgM?
- Pentamer

what is the structure of IgA?
dimeric

what is the first antibody isotype produced in an immune response? Why?
- IgM
- Because it is a pentamer, it has 10 antigen binding sites
- It binds with high avidity and can produce a strong response
What are the 3 ways that antibodies participate in immune response?
- Neutralization - bind pathogen/toxins to prevent the pathogen binding to host cells
- Opsonization - bind pathogen directly to mark it for phagocytosis
- Activate complement system - results in lysis and phacocytosis
Which antibodies participate most in neutralization? Why?
- IgG
- IgA
- These are high affinity antibodies
Where is IgA found?
- Mucosa (respiratory tract, GI tract)
Examples of IgA participating in host defense via neutralization
- Strep
- Influenza
Which antibodies participate in complement fixation?
- IgM - C1q binds to IgM and initiates classical pathway
- IgG - C1q binds to two or more IgG and initiates classical complement pathway