Wk 6 GI Embryology & Anatomy/Phys Flashcards
(88 cards)
The primitive gut tube is derived from the extraembryonic part of embryo’s yolk sac. True or false.
False
Extraembryonic yolk sac = 2ndary yolk sac –> provides nutrients to the embryo while utero-placental circulation is estsablished; later assimilited into umbilical cord.
Intraembryonic yolk sac = primitive gut
How is the gut tube formed from the 3 germ cell layers?
Endoderm: epithilial lining of digestive tube & digestive organs (liver, gallbladder, & pancreas) arise as buds
Mesoderm: through lateral folding, eventually surrounds the gut tube forming connective tissue & muscular walls.
Ectoderm: forms the neural tube that gives rise to the neural crest cells that invade the mesoderm forming neurons & glial cells intrinsic to GI tract

What are the 3 parts of the endodermal gut tube?
Foregut, midgut, & hindgut
What parts of the digestive system arises from the foregut?
Esophagus, stomach, proximal duodenum (to ampulla of Vater)
Liver/biliary apparatus
Pancreas
What artery supplies blood to the foregut?
Celiac

What parts of the digestive system arise from the midgut?
Small intestine (including duodenum distal to the bile duct)
Part of the large intestine: cecum, appendix, ascending colon & proximal transverse colon (2/3 of transverse colon)

What artery supplies blood to the midgut?
Superior mesenteric

What parts of the digestive system arise from the hindgut?
Large intestines: distal transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, superior part of anal canal
What parts of the endodermal gut tube (foregut, midgut, & hindgut) give rise to organs that are not part of the digestive system?
Foregut = Lower respiratory system & pharynx –> in the book known as a 4th section of the primitive gut, the Pharyngeal gut (includes the 2 mentioned above & the upper esophagus), the foregut is the lower esophagus down
Hindgut = epithelium of urinary bladder & most of urethra
What eventually forms into the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas?
Duodenal buds
By the 4th-6th week, what is a major early hematopoietic organ of the embryo?
Liver
When does the bone marrow take over hematopoiesis from the liver?
Approx 6 months
At birth a child’s liver is equivalent to an adult’s size. True or false.
False, at birth, the liver is 20% of the adult size –> will continue to grow for 25-30 years.
What attaches the liver to the ventral wall?
Falciform ligament

What is the respiratory diverticulum?
Lung bud
In the embryo, arising frm the foregut, the respiratory diverticulum grows from the ventral wall of the esophagus at its border with the pharyngeal gut.
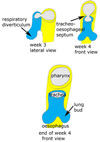
What is the esophagotracheal septum?
The separation between the respiratory diverticulum & the foregut portion that eventually becomes the esophagus

What are the 4 layers of the GI tract? (inside to outside, include the sublayers)
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, & serosa

Mucosa (epithelium, lamina, muscularis mucosae)
Submucosa
Muscularis (Circular muscle layer, longitudinal muscle layer)
Serosa (connective tissue layer, peritoneum)
By which week of gestation does the respiratory diverticulum separate from the foregut that eventually becomes the esophagus?
Wk 4
What are the steps forming the enteric nervous system?
1) neural crest cells enter the gut
2) crest cells proliferate
3) crest cells migrate along the gut
4) crest cells differentiate & form connections w/ their targets.
How is the GI tract innervated?
ANS - sympathetic slows it down, parasympathetic (vagus nerve) speeds it up
Also have intrinsic innervation - submucosal plexus (Meissner plexus) & myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus)
Describe the innervation of the stomach.
Extrinsic - originate outside stomach –> parasympathetic fibers frm vagus nerve & sympathetic fibers frm the celiac plexus
Intrinsic - originate w/in stomach & respond to local stimuli –> myenteric plexus

What is peristalsis?
Coordinated sequential contraction & relaxation of the outer longitudinal & inner circular layers of muscles.
What gestation age does the gut develop normal propulsive motility/peristalsis?
30 wks
What gestational age can you swallow?
11-12 wks