Y2S1 Anatomy Flashcards
(73 cards)
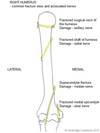
Which nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the upper arm?
Musculocutaneous
What are the muscles of the anterior compartment of the upper arm?
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Coracobrachialis
(all have “brachi-“ in their name”

What is the muscle in the posterior compartment of the upper arm?
Triceps brachii
Which nerve innervates the posterior compartment of the upper arm?
Radial
Which muscles are innervated by the axillary nerve?
Deltoid
Teres minor
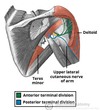
How many muscles are in each layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Superficial - 4
Intermediate - 1
Deep - 3
What are the superficial muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (“the superficial flexors”)?
Pronator teres
Flexor carpi radialis
Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Pass Fail Pass Fail

Which muscle lies in the intermediate compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Which muscles lie in the deep compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor pollicis longus
Pronator quadratus
Act to pronate the wrist and clench your fist
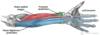
Which muscles of the anterior forearm are NOT innervated by the median nerve and are innervated by the ulnar nerve?
Medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor carpi ulnaris
The median nerve innervates which hand muscles?
Thenar muscles (flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis)
Lateral two lumbricals of the hand
LOAF: Lateral Lumbricals, Abductor pollicis brevis, Opponens pollicis, Flexor pollicis brevis
The median nerve innervates the lateral lumbricals and the thenar muscles of the hand. Which nerve innervates the remainder of the hand muscles?
Ulnar nerve
Which nerve innervates the forearm extensors?
Radial nerve (innervates all the muscles on the posterior side of the arm)
What are the superficial muscles in the posterior forearm?
Brachioradialis
Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis
Extensor digitorum
Extensor digiti minimi
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Anconeus

What are the deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?
Supinator
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis longus and brevis
Extensor indicis

Which compartment of the lower limb does the femoral nerve supply?
Anterior thigh muscles - flexion of the hip and extension at the knee
Like you’re kicking a soccer ball
The obturator nerve innervates which compartment of the lower limb?
Medial compartment of the thigh - adductors
The sciatic nerve innervates which compartment of the lower limb?
Posterior thigh
Its branches innervate the leg and foot
Innervation to the leg and foot is provided by branches of which major nerve?
Sciatic
What are the two major branches of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial nerve
Common fibular (peroneal) nerve - which branches to form the deep and superficial fibular nerves
Which compartments of the leg are innervated by the two major branches of the fibular nerve?
Superficial fibular - lateral compartment of the leg
Deep fibular - anterior compartment of the leg and foot muscles
Which compartment of the leg is innervated by the tibial nerve?
Posterior
Name 4 places where hyaline cartilage is found
- Nose
- Parts of the respiratory tract e.g. tracheal rings
- Ends of ribs
- Articular surfaces of bones
+ developing foetus, precursor to bone deposition
What type of collagen predominants in hyaline cartilage?
II