Chapter 3 Flashcards
Arithmetic mean of a Sample
The sample mean is the sum of the values in a sample divided by the number of values in the sample symbol: x̄
Where:
x̄ = sample mean
n = number of values or sample size
xi = ith value of the variable x
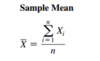
Median
The middle value in an ordered array of data that has been ranked from smallest to largest. Half the values are smaller than or equal to the median, and half the values are larger than or equal to the median.
There are two rules for computing the Mean
- Rule 1 If the data set contains an odd number of values, the median is the measurement associated with the middle-ranked value
- Rule 2 If the data set contains an even number of values, the median is the measurement associated with the average of the two middle-ranked values.

Geometric Mean
The geometric mean is the nth root of the product of n values:
x̄G = (x1*x2*x3…*xn)1/n
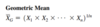
Geometric Mean Rate of Return
The geometric mean rate of return measures the mean percentage return of an investment per time period
ṜG = [(1+R1)*(1+R2)*…*(1+Rn)]1/n - 1
where
R<em>i</em> = rate of return in time period i
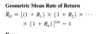
Range
The range is equal to the largest value minus the smallest value.
Range = Xlargest - Xsmallest
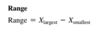
Sample Variance
S2
The sample variance is the sum of the squared differences around the mean divided by the sample size minus 1

Sample Standard Deviation
S
The sample standard deviation is the square root of the sum of the squared differences around the mean divided by the sample size minus 1

Coefficient of Variation
The coefficient of variation is equal to the standard deviation divided by the mean, pultiplied by 100%
Where
S = sample standard deviation
x̄ = sample mean
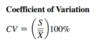
Z Score
The Z score for a value is equal to the difference between the value and the mean, divided by the standard deviation
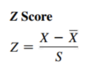
First Quartile, Q1

Third Quartile, Q3

Interquartile Range

The Five Number Summary
Xsmallest Q1 Median Q3 Xlargest
Population Mean
The population mean is the sum of the values in the population divided by the population size, N
where
- µ = population mean
- Xi = ith value of the variable X
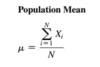
Population Variance
The population variance is the sum of the squared differences aroudn the population mean divided by the population size, N





