13 ⼀PEDIATRICS COPY Flashcards
(130 cards)
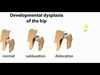
What is the treatment for Developmental Dysplasia of Hip?
Pavlik Harness tat holds hip in flexion and ABduction

What demographic is affected by Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis ?
[3-6 week old boys]
describe Puberty timeline for females (4)
[8-12 yof: breast + pubic hair]
–(within 2.5y)–>
growth spurt ->
MENARCHE
_________________
1º amenorrhea = NO MENSES + ([≥15y with F∆] or [≥13y with no F∆])
What does Constitutional Short Stature refer to
“late bloomer” but will attain normal adult height later
pts have normal birth wt and ht but ht velocity slows between 6 mo-3 yo, picks back up after and slows again at adolescence. bone radiographs will show delayed bone age
[Genu Varum] is normal during age ⬜ and presents as (⬜3) . When should this correct by?
0-2 yo ; [BL symmetric bow leg, normal stature, no lateral thrust]
_________________
should correct by 2 yo

obtain XR if > 2 yo, short stature or uL
Newborn failure to pass meconium within 48 hours of birth likely indicates ⬜
MOD
Hirschsprung Disease
________________
[absence of ganglion cells in rectosigmoid (confirmed by rectal suction biopsy)] ➜ transition zone cutoff between
[narrow aganglionic rectosigmoid] and [markedly dilated innervated descending colon] EARLY AFTER BIRTH

Craniopharyngioma etx
Calcified low grade malignancy dervied from epithelial remnants of Rathke pouch within the pituitary stalk and reside in the SUPRAsellar region
Marfan Syndrome and Ehlers Danlos can present similarly
How do you discern the two?-2 ; What is the etx for Ehlers Danlos?
“Marfan BAATHES a lot! “
BUT Ehlers Danlos does NOT have
- Ectopia Lentis
- Arm-to-Height Ratio that’s INC
Ehlers Danlos etx = defective collagen production
diagnostic criteria for suspected septic joint
_________________
empiric abx for septic joint
[WBC >50Kneutrophil predominance] in [aspirated joint synovial fluid]
_________________
Vanc IV
cp for [Measles rubeOla] -2
[fever + conjunctivitis + coryza + Koplik spots + cough] prodrome –(2-4days)–> [maculopapular rash sspreading head to body]
________________
tx = supportive +/- [Vitamin A if hospitalized]

After successfully treating Acute Otitis Media, how should you manage a patient who p/w persistent middle ear fluid build up?
_________________
Explain why
WATCHFUL WAIT X 3 MO after treatment
_________________
serous fluid may persist in middle ear up to (but usually self limited to) 3 mo after treatment (= [serous otitis media with effusion] ).
further w/u if: infection / BL effusion / sx > 3 mo

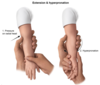
Risk factors for Developmental Dysplasia of Hip - 3
________________
when should you stop screening for this?

- Breech Delivery - GET HIP IMAGING IF FEMALE AND BREECHED
- Female - GET HIP IMAGING IF FEMALE AND BREECHED
- Fam hx
12 months old

Dx Criteria for Kawasaki Disease
{[4/5 CRASH] + [Burning HIGH Fever ≥ 5 days]}
- Conjunctivitis
- Rash
- Adenopathy uL in cervical region (least likely)
- Strawberry tongue/oral mucosa changes
- Hand/Feet redness or swelling
- THIS IS DX OF EXCLUSION! THERE CAN NOT BE ANOTHER OBVIOUS CAUSE OF PRESENTATION*
Meckel’s Diverticulum etx
tx = surgery
failure of vitelline duct to obliterate during first 8 WG ➜ leaves behind RLQ [ectopic gastric tissue in a blind pouch] ➜ mucosal irritation and bleeding from gastric acid➜ [PAINLESS HEMATOCHEZIA IN 2 Y/O]

Malrotation and Volvulus are both diagnosed with ⬜
Describe how both would look on this diagnostic?
Upper GI Series barium swallow
________________
Malrotation = Ligament of Treitz on the R side of the abd in a gasless abd
________________
Volvulus = corkscrew image on barium swallow Upper GI series

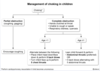
management of
pediatric functional constipation (3)
1st: dietary ∆
2nd: Osmotic Laxatives
ACUTE DISIMPACTION: STIMULANT LAXATIVE
_________________
dietary ∆ = [⇪ fiber/water] | [cow’s milk< 24oz]
How do you manage infants born to Mothers with Active Hepatitis B (4)
_________________
How do you determine if the infant was vertically infected?
infant receives
- [AT BIRTH (within 12h of delivery) [HBVIG and HBVV1]]
- [2 mo HBVV2]
- {[6 mo HBVV3]
- –(3 months later)–> [9 mo obtain HBV Surface antigen]}
_________________
if [HBsAg] positive = HBV VERTICALLY INFECTED!

Annual Influenza vaccine is recommended for kids age ⬜ for what purpose?
≥6 month old ; prevent [infection and spread] to at-risk populations (asthma/chronic illness/<2 yo)
Hypetrophic Pyloric Stenosis cp (6)
- age 3-6 weeks old
- [POSTPRANDIAL PROJECTILE NONBILIOUS EMESIS]
- [“Hungry Vomiter” (hunger immediately after vomiting)]
- [Epigastric Palpable Olive mass]
- Visible peristalsis
- [hypOchloremic hypOkalemic metabolic alkalosis]
_________________
[dx = US] | [tx = IVF ➜ Pyloromyotomy]
FPIAP is a ⬜ reaction to ⬜ that presents in normal infants as ⬜ . The treatment in formula-fed infants is ⬜
FPIAP = Food Protein Induced Allergic Proctocolitis
[non-IgE allergy] ; [milk protein (cow’s milk or soy protein)] ; blood-streaked stools ; Extensively Hydrolyzed Formula

FPIAP = non-IgE rxn to milk protein (casein/whey) = no skin/pulm rxn
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis is a complication of childhood obesity
When does this present?
________________
How does this present?
________________
dx?

puberty (most common hip disorder in fat teens!)
________________
[M: Months of vague hip/knee pain] without acute onsets
________________
pelvis XRay
fat teen ➜ [ANT SUP slippage of femoral neck] ➜ [POST INFERIOR displacement of Femoral head] ➜ [Months of vague hip/knee pain]

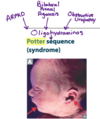
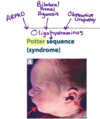
Oligohydramnios –> ⬜ sequence.
Name the 3 most common causes of Oligohydramnios
Oligohydraminos –> POTTER Sequence
POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES are the most common cause of obstruction in newborn boys (which causes renal damage –> oligohydramnios during utero)

Oligohydramnios –> ⬜ sequence.
Name the 3 most common causes of Oligohydramnios
Oligohydraminos –> POTTER Sequence
POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES are the most common cause of obstruction in newborn boys (which causes renal damage –> oligohydramnios during utero)
What is [Impetigo Diaper Dermatitis]?
________________
Tx? -3
secondary bacterial diaper infection (by Staph > GASP) characterized by honey-crusted papules and pustules (and in neonates can be c/b sepsis)
________________
- skin :* [Topical Mupirocin] or [PO Cephalexin]
- [skin+ sepsis s/s]*: [Admit for IV Abx and sepsis w/u]
________________
sepsis s/s = [neonatal fever/irritability/lethargy]