4 ⼀PREGNANCY/BREAST/REPRO Z Flashcards
(496 cards)
etx for Gestational Transient Thyrotoxicosis
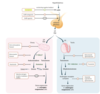
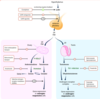
βhCG shares α subunit with TSH.
during pregnancy, ⇪ [fetal βhCG] stimulates [Maternal Thyroid gland TSH receptors] ➜ [⇪ TOTAL Maternal T4 and T3] secretion
In [Gestational Transient Thyrotoxicosis], [Multiple gestation or hyperemesis gravidarum] ➜ VERY high [fetal βhCG] ➜ [⇪ ⇪ ⇪ TOTAL Maternal T4 and T3] that resolves by 16WG
What is Asherman syndrome?
[Intrauterine adhesions and endometritis] from uterine instrumentation (D&C) ➜ [cyclic abd pain and secondary amenorrhea] immediately following instrumentation
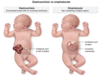
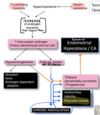
Choriocarcinoma (the most aggressive kind of ⬜ ) can follow any type of ⬜ and presents with ⬜-4
________________
What 2 locations does Choriocarcinoma occur?
[gestational trophoblastic neoplasia] ; pregnancy ;
[AFTER PREGNANCY ➜ irregular vaginal bleeding + enlarged uterus + positive pregnancy test]
________________
Vagina | Lung

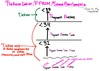
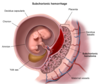
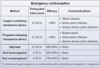
Major causes of Antepartum Hemorrhage - 3
Antepartum = right before childbirth
- Placental abruptio (PAINFUL Anterpartum hemorrhaging)
- Placental previa
- Vasa Previa

CP for Placental Abruptio - 4
Risk factors = HTN, cocaine, smoking, prior abruptio, abd trauma
- sudden PAINNNFFULLL antepartum vaginal bleeding (which can –> hypovolemic shock, [DIC-from decidual bleeding releasing tissue factor 7] and fetal demise) - (UNLESS CONCEALED = then no vag bleeding)
- Distended firm uterus
- abd AND/OR back pain
- [contractions of low intensity]
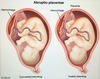
etx: HTN of maternal decidual vessels –> rupture –> premature detachment of placenta from endometrium
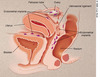
pregnant patient 35 WG p/w painless vaginal bleeding
Next step is (⬜ Digital Cervical Exam | TVUS) and why?
TVUS

s/f Placenta PREVIA, in which digital Cervical Exam is contraindicated since it enters endocervical canal. TVUS and speculum do NOT enter endocervical canal
_________________
Placenta Previa
Of the 3 placental demise, which is a/w painLESS antepartum vaginal bleeding?
Placenta Previa

Recurrent UTI refers to (⬜2)
________________
Tx?
[≥2UTI in 6 mo]
or
[≥3UTI in 12 mo]
________________
Postcoital abx prophylaxis
(Bactrim, nitrofurantoin, cephalexin, cipro)
Amniotic Fluid Embolism tx
supportive
__________________________________
release of fetal amniotic fluid into maternal circulation (during labor or immediately postpartum) ➜ maternal massive inflammatory response that causes acute hypoxemia, hypotension, DIC
Amniotic Fluid Embolism etx
_________________
What are the 2 major risk factors for this?
release of fetal amniotic fluid into maternal circulation (during labor or immediately postpartum) ➜ maternal massive inflammatory response that causes acute
hypOxemia
[hypOtension 2/2 obstructive shock]
DIC
_________________
Placenta Previa and Placenta Abruptio
After the Rupture of Membranes, when is it safe for labor to begin?
[1 - 18 hours after ROM] (no sooner ; no later)
________________
labor starting ≥18H after ROM ➜ chorioamnionitis ➜ neonatal sepsis
________________
- Do not confuse this with PPROM (Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membrane)*
- Chorioamnionitis Tx = Abx –> Delivery*
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes (which occurs before 37 WG)
How do you manage PPROM when it occurs ≥ 34WG?
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
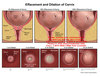
Define Preterm Labor

regular uterine ctx that ➜ cervical diLation < 37 WG

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
[Betamethasone antenatal CTS] is given to pregnant patients with [PPROM/Preterm labor]/Severe Preeclampsia] before 37 WG
_________________
What are the 4 major benefits of using [Betamethasone antenatal CTS]?

[Betamethasone antenatal CTS] ⬇︎
- NRDS
- IVH
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Neonatal mortality from prematurity
_________________
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
How do you manage [PPROM < 34 WG] when it occurs
abx = [PCN + azithromycin]

if baby not compromised, fetal surveillance until 34 WG and then deliver!
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio
Full term infant = 37- 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG - 2
Pregnant Bitches
When are pts screened for Group B Strep via vaginal and rectal swab?
36-38 WG
results are valid for 5 weeks
When does a breech pregnant patient become eligible to receive [External Cephalic Version]?
≥37 WG
Sickle Cell Disease patients who are pregnant are at ⇪ risk for developing ⬜ , which presents with what 4 s/s ?
_________________
how is this different from [Acute fatty liver of pregancy]? (2)
[Acute Sickle Hepatic Crises 2/2 vasooclusive crisis]
- [RUQ pain w/ slight transaminitis]
- [sickle hemolysis (anemia/jaundice/icterus)]
- NV
- fever
_________________
SAME AS AFLP except…
AFLP = 3rd trimester and AFLP = [TRANSAMINITIS SIGNIFICANT > 300]
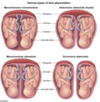
[Recurrent pregnancy lost] is defined as ⬜ . What heme/onc abnormality is a/w [Recurrent pregnancy lost]?
how is it managed?
[≥3 consecutive 1st trimester (< 20WG) spontaneous abortions]
_________________
Antiphospholipid syndrome (ASA for thrombosis px)
[Recurrent pregnancy lost] is defined as ⬜ . What anatomical abnormality is a/w [Recurrent pregnancy lost]?
how is it managed?
[≥3 consecutive 1st trimester (< 20WG) spontaneous abortions]
_________________
Uterine septum (tx = hysteroscopic surgical resection)
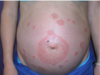
What is shoulder dystocia? how does it present?
_________________
management? (6)
initial failure to deliver fetal ANT shoulder = OBSTETRIC EMERGENCY!
p/w fetal head retraction into perineum after head delivers
_________________
B.E. C.A.L.M.

Screening for gestational DM is done ⬜ WG
_________________
how is gestational DM screening done?
24-28WG
_________________

inadequate control of gestational DM ➜ ⬜ and ⬜
_________________
Tx for gestational DM? (3)
fetal macrosomia / shoulder dystocia
_________________

1st: diet
2nd: INSULIN
–(alternative)–> [PO glyburide vs metformin]