Lecture 10 Flashcards
What bones make up the hip bone?
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
What are the functions of the Pelvis or “hip bone”?
support the abdominal contents
forms attachemnt for the legs
forms attachment for abdominal muscles
What is A?
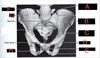
Posterior Superior Iiliac Spine
What is B?

Anterior Superior iliac Spine
What is C?

Anterior Inferiror Iliac Spine
What is D?

Acetabulum
What is E?
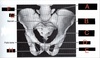
Pubic symphysis
What is F?

Crest of Ilium
What is G?

Ilium
What is H?

Ischium
What is the most important muscle for inspiration?
Diaphragm
What is the origin and insertion of the external intercostals
Origin: upper rib (tubrical)
Instertaion: rib below it
What is a hiatal hernia?
when the stomach starts pushing up through the esophageal hiatus
What makes up the pelvic girdle?
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis (Pubic Bone)
What is the attachement for legs on the pelvic girdle?
acetavulum

